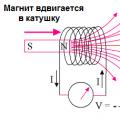
The ability to control the movement of an object is the stuff of science fiction, but thanks to researchers at the Minnesota College of Science and Engineering, it has become a reality. Using a non-invasive technique known as electroencephalography, which uses brain waves, five students were able to control the movement of a helicopter.
By looking in the opposite direction from the helicopter, students were able to move the vehicle in different directions, imitating the movements of the left hand, right hand, and both hands. After some time, the project participants were able to perform several maneuvers with the helicopter, including passing through the ring. Scientists hope to improve this non-invasive technology for manipulating brain waves, which will ultimately help restore movement, hearing and vision in patients suffering from paralysis or neurodegenerative disorders.
MRI of the heart

Anthracycline remains an effective form of chemotherapy, but it has been shown to damage the hearts of children undergoing treatment. Typically, most children affected by this heart defect were found to have thinned the walls of their hearts, and by the time they were diagnosed, it was too late to do anything about it. Ultrasound often misses heart defects in the early stages of the study and detects them only when irreversible damage has already taken its toll.
Last year, a fundamentally new technology appeared. Extensive testing has shown that T1 MRI may be a more accurate, effective and safer method for detecting cardiovascular disease in children. Doctors were able to see children's heart defects earlier and more effectively than with ultrasound (which erroneously shows that the heart is doing fine). This is an excellent medical advance for detecting heart disease in young children.
Efficient electrolysis (salt water splitting)

In the race to find efficient and rich alternative fuels, researchers are constantly trying to find a way to efficiently split seawater to produce hydrogen fuel. Last June, a team at the Australian Electromaterials Science Research Center unveiled a catalyst that could split ocean water using little energy.
The catalyst was implemented in a flexible plastic tank that absorbs and uses energy obtained from light to oxidize seawater. Unlike existing methods, which require large amounts of energy to oxidize water, this method can generate enough energy to power the average home and car for an entire day using only 5 liters of seawater.
This tank contains synthetic chlorophyll molecules that harness the sun's energy in the same way that plants and algae do. There are no chemical problems with this method either, unlike the current water splitting method, which releases clouds of poisonous gas - chlorine.
This efficient and effective method can significantly reduce the cost of hydrogen fuel, allowing it to become a gasoline-competitive alternative fuel in the future.
Tiny battery

With the invention of 3D printers, the limits on the types of complex and complex objects that can be created have expanded significantly. Last year, a team of researchers from Harvard and the University of Illinois were able to synthesize a lithium-ion battery that is smaller than a grain of sand and thinner than a human hair.
Such amazing dimensions were achieved using a thin layering of a network of intertwined electrodes. Once the 3D design was made on the computer, the printer used specially made liquid inks containing electrodes that were supposed to harden immediately when exposed to air. There are many uses for such a device, all thanks to its size. However, 3D printers already have a circulatory system, so few people will be surprised by electrodes.
Before the advent of this battery, the existence of incredibly small battery-powered objects was virtually impossible. The fact is that to create such batteries, similar batteries were needed that could first transfer energy. The 3D printer uses ink and a detailed design from a computer program to create microbatteries like these.
Bioengineered body parts

On June 6, 2013, a team of doctors at Duke University successfully implanted the first bioengineered blood vessel into a living patient. Although bioengineering is advancing by leaps and bounds, this procedure was the first successful implantation of an artificial bioengineered body part.
The vein was implanted in a patient suffering from end-stage kidney disease. First, it was synthesized from a human donor cell on a kind of “scaffolding.” In order to prevent the foreign body from being attacked by any antibodies in the patient, the qualities that could provoke this attack were removed from the vein. And the vessel was more successful than synthetic or animal implants because it was not prone to clotting and did not pose a risk of infection during surgery.
Incredibly, the veins are made from the same flexible materials that connect them, and also take on properties from the cellular environment and other veins. With the success of such a procedure, this new field has enormous implications for future developments in the world of medicine. In addition, in 10-15 years a bioengineered heart will be printed, if forecasts are to be believed.
Four-quark particle

The search for an explanation for the birth of our Universe has been significantly heated by last year's announcement of the discovery of a particle made of four quarks. While this finding may not seem like a big deal to you, for physicists it raises a number of new explanations and theories about the creation of the first matter. Until then, explanations for the creation of matter had been significantly limited by the fact that only particles with two or three quarks had been discovered.
Scientists have named the new particle Zc (3900), and they believe it was created in the first, frenzied seconds after the Big Bang. After several years of complex mathematical calculations carried out by the BaBar collaboration at the SLAC National Acceleration Laboratory (affiliated with Stanford University), scientists working at the Beijing Electro-Positron Collider (BEPCII) discovered this particle in a number of cases. Since scientists are generally very generous people, the results were shared with the guys at CERN and HEARO in Tsukuba. These are the same scientists who recently observed and isolated 159 similar particles. However, the particle lacked substantiation until scientists at the Belle detector in Beijing confirmed the identification of 307 individual particles of this type.
Scientists say it took 10 trillion trillion subatomic collisions in their detector, which is twice the size of the famous Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland. Some physicists have criticized the observations, arguing that the particle is nothing more than two mesons (two quark particles) joined together. Despite this, the particle was accepted.
Alternative microbial fuel

Imagine a world where highly efficient, low-cost alternative fuels could be obtained as easily as oxygen from the air around us. Thanks to a collaboration between the US Department of Energy and a team of researchers at Duke University, we may have microorganisms that make the dream a reality. Recent years have seen increasing advances in the world of alternative fuels (ethanol from corn and sugar cane, for example). Unfortunately, these methods are very ineffective and do not stand up to criticism. Not long ago, scientists were able to come up with an electric fuel that could “eat” solar energy without robbing us of water, food or land, like most alternative fuels.
In addition to low energy requirements, tiny microbes can efficiently synthesize these electrofuels in the laboratory. Electrofuel microbes have been isolated and found in non-photosynthetic bacteria. They use electrons in the soil as food and consume energy to produce butanol by interacting with electricity and carbon dioxide. Using this information and some gene manipulation, the scientists incorporated this type of microbe into laboratory-grown bacteria cultures, allowing them to produce butanol in huge quantities. Butanol now looks like a better alternative to both ethanol and gasoline for a variety of reasons. Being a larger molecule, butanol has greater energy storage capabilities than ethanol and does not absorb water, so it can easily be found in the gas tanks of any car and transferred through gasoline pipelines. Butanol microbes have become a promising beacon for the era of alternative fuels.
Medical Benefits of Silver

A study on the benefits of using silver in antibiotics was published on June 19 last year by Boston University researchers. While silver has long been known to have strong antibacterial properties, scientists have only recently discovered that it can turn conventional antibiotics into antibiotics on steroids.
It is now known that silver uses a variety of chemical processes to inhibit bacterial growth, slow down their metabolic rate, and disrupt homeostasis. These processes weaken the bacteria and make them more susceptible to antibiotics. Multiple studies have shown that a mixture of silver and antibiotics was up to 1000 times more effective at killing bacteria than antibiotics alone.
Some critics warn that silver can have toxic effects on patients, but scientists disagree, arguing that small and non-toxic amounts of silver only increase the effectiveness of antibiotics without causing harm in treatment. This is a very interesting discovery for the medical world, and the use of precious metals continues to develop in quantitative and qualitative terms.
Vision for the blind

The first prototype of a bionic eye by a team of Australian bioengineers in early June last year. The bionic eye works using a chip implanted in the user's skull and then connected to a digital camera in the glasses. While the glasses currently only allow the user to see outlines, the prototype should improve significantly in the future. Once the camera captures an image, the signal is modified and sent wirelessly to the microchip. From there, the signal activates points on a microchip implanted in the part of the cerebral cortex responsible for vision. The team of researchers hopes that in the future, glasses that are lightweight, comfortable and unobtrusive can provide maximum comfort to people with low vision. They can be used by 85% of blind people.
Immunity to cancer

Last year, the University of Rochester looked at the cancer-fighting mechanism of naked mole rats. These creepy underground rodents are not the cutest on this planet, but they will be the ones who will have the last laugh when all living things die of cancer.
A sticky sugar, hyaluronan (HA), has been found in the spaces between the cells of naked mole rats' bodies and appears to prevent cells from growing closely and forming tumors. Roughly speaking, this substance stops the proliferation of cells as soon as they reach a certain density. The reason for the increased amount of this sugar is, scientists think, a double mutation in two enzymes that promote the growth of HA.
It was found that in a cell with a low level of HA, cancer grows rapidly, but in cells with a high level of HA, a tumor does not form. Scientists hope to modify laboratory rats to produce large amounts of HA and make them immune to cancer.
It often happens that we go to the doctors and the news that we need surgery takes us by surprise. We are very afraid and begin to delay this moment, thereby making it even worse. Let us ask ourselves the question: -What are we afraid of? ..
2019-07-18 726 0 Scientific discoveries
An international team of physicists has discovered why beta decays in atomic nuclei occur more slowly than in free neutrons. Scientists have been struggling to solve this mystery for 50 years, according to a press release on Phys.org. Researchers studied the transformation of the isotope tin-100 into indium-100. These two elements have the same...
2019-03-12 958 0 Scientific discoveries
Physicists from the USA and China have for the first time calculated the contributions to the proton mass associated with various effects. For calculations performed within the framework of lattice QCD, scientists used the Titan supercomputer with a performance of about 27 petaflops. As a result, the researchers found that the quark condensate provides about..
2019-02-26 860 0 Scientific discoveries
Physicists from Germany proposed using electromagnetic waves with azimuthal polarization to overcome the diffraction limit and accurately measure the position of a nanoparticle on a glass substrate. By observing the scattering of such waves on a spherical particle, scientists were able to record a displacement of just...
2019-02-26 676 0 Scientific discoveries
The Wendelstein 7-X stellarator proved its performance in a series of experiments conducted in 2016-2017 - the plasma-destabilizing booster current was reduced by almost four times, and the plasma confinement time was increased to 160 milliseconds. This is currently the best result among stellarators. ..
2018-06-04 22858 0 Scientific discoveries
Physicists at the University of Maryland have discovered an exotic superconductor, YPtBi, inside which electrons interact with each other to form high-spin quasiparticles. This was reported in the journal Science Advances. Scientists analyzed the electronic structure of a material made from yttrium, platinum..
2018-04-10 7614 0 Scientific discoveries
Physicists from Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have identified the mechanism of operation of the anomalous superconductor strontium titanate, which is capable of conducting electricity without resistance despite the fact that it is not a metal. Science Alert reports this. Strontium titanate is an oxide, however...
2018-03-27 5869 0 Scientific discoveries
Mathematicians from the University of California at Berkeley have found a condition for the existence of naked singularities in black holes, in which the laws of physics are violated. This conclusion calls into question the strong principle of cosmic censorship, when a naked singularity should be unattainable for any...
2018-03-06 6709 0 Scientific discoveries
Neurologists from the Charite University Hospital in Berlin have revealed the processes occurring in the human brain during the dying process. It turned out that the “brain tsunami” - a wave of depolarization of nerve cells that spreads uncontrollably across the cerebral cortex and causes the death of neurons - can be blocked. ..
2018-03-06 6784 0 Scientific discoveries
American physicists were the first to experimentally register bound states of three photons. The formation of trimers, unusual for photons, occurs when a laser beam passes through a cloud of cooled rubidium atoms due to the formation of intermediate polariton states, scientists write in Science. In contrast..
2018-02-18 4967 0 Scientific discoveries
Scientists at Northwestern University in the US have found that terminally ill people suffering from Huntington's chorea have an 80 percent reduced risk of cancer. It turned out that tumor cells are sensitive to a defective form of the huntingtin protein, which also causes the death of nerve cells. This is reported...
2018-02-14 5882 0 Scientific discoveries
Biologists from Moscow State University have discovered a “molecular timer” - a special mechanism for regulating protein synthesis that prevents the formation of abnormal molecules through stuck ribosomes. According to scientists, the discovery will help create therapeutic methods to combat cancer. This was reported in a press release...
2018-02-05 5322 0 Scientific discoveries
Scientists at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have deciphered the genome of one of the simplest multicellular life forms - the green algae Tetrabaena socialis, consisting of four cells. This made it possible to identify the genetic mechanisms that contributed to the emergence of multicellularity. An article by biologists was published in the journal..
2018-02-05 4663 0 Scientific discoveries
Hypothetical magnetic monopoles could be created in collisions of heavy ions or in the strong magnetic fields of neutron stars. Physicists from Imperial College London theoretically examined these processes and calculated the lower limit for the possible mass of monopoles - it turned out to be slightly less than the mass..
2017-12-14 4165 0 Scientific discoveries
Physicists have developed a shell that, due to magnetohydrodynamic effects, makes it possible to completely suppress all disturbances in the flow of water around moving objects. In a paper published in Physical Review E, the scientists also proposed a way to create such a device that could...
2017-12-12 4038 0 Scientific discoveries
For the first time, physicists have experimentally measured the force of attraction that acts on individual cesium atoms from a black body. This force turned out to be several times greater than the gravitational force and the pressure force of electromagnetic radiation, write the authors of the work published in Nature Physics. Effect..
2017-12-11 3749 0 Scientific discoveries
An international team of researchers has proven the existence of a new form of matter - excitonium. It is a condensate of excitons—electrons and “holes” bound together. This state of matter was first predicted almost 50 years ago. The scientists' article was published in the journal Science. About it..
2017-12-11 4564 0 Scientific discoveries
An international team of physicists has managed to reverse the passage of time for a pair of interconnected particles. Researchers have proven that for quantum interconnected qubits (quantum bits) the second law of thermodynamics is spontaneously violated, according to which in isolated systems all processes proceed only in the direction of increasing...
2017-12-05 3305 0 Scientific discoveries
An extended version of the main physical theory, the Standard Model, predicts that charged particles can polarize the vacuum and emit photons. The Brazilian theoretical physicist studied this effect, known as vacuum Cherenkov radiation, and used it to set limits on certain parameters.
2017-11-30 3256 0 Scientific discoveries
Professor of the Nizhny Novgorod State University named after Nikolai Lobachevsky, Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Yaroslav Sergeev, in an interview with TASS, announced the solution to two Hilbert problems. The research was published in the journal of the European Mathematical Society EMS Surveys in Mathematical Sciences. The first problem, about the solution..
2016 was rich in high-profile scientific discoveries and spectacular technical achievements. The discoveries are widely covered in the media, and the most interesting new gadgets were demonstrated at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES). For 50 years now it has been a launching pad for innovation and hi-end technologies.
December has arrived and it's time to sum it up the most interesting results of 2016 in science and technology.
Top 10 most notable scientific achievements of 2016
10. Multicellular life is the result of genetic mutation
The GK-PID molecule allows cells to divide, avoiding malignant formations. At the same time, the ancient gene, an analogue of GK-PID, was a building enzyme necessary for the creation of DNA. Scientists have suggested that in some ancient single-celled organism 800 million years ago the GK gene was duplicated, one of the copies of which then mutated. This caused the appearance of the GK-PID molecule, which allowed cells to divide correctly. This is how multicellular organisms appeared
9. New prime number
 It became 2^74,207,281 – 1. The discovery is useful for cryptography problems where both very complex and simple Mersenne numbers are used (49 of them were discovered in total).
It became 2^74,207,281 – 1. The discovery is useful for cryptography problems where both very complex and simple Mersenne numbers are used (49 of them were discovered in total).
8. Planet Nine
 Scientists from the California Institute of Technology have provided evidence that there is a ninth planet in the solar system. Its orbital period is 15,000 years. However, due to its colossal orbit, not a single astronomer was able to see this planet.
Scientists from the California Institute of Technology have provided evidence that there is a ninth planet in the solar system. Its orbital period is 15,000 years. However, due to its colossal orbit, not a single astronomer was able to see this planet.
7. Eternal data storage
 This 2016 invention was made possible thanks to nanostructured glass, on which information is recorded using ultra-high-speed short and laser pulses. The glass disk holds up to 360 TB of data and can withstand temperatures up to a thousand degrees.
This 2016 invention was made possible thanks to nanostructured glass, on which information is recorded using ultra-high-speed short and laser pulses. The glass disk holds up to 360 TB of data and can withstand temperatures up to a thousand degrees.
6. Relationship between the blind eye and four-toed vertebrates
 A fish called the Taiwan blind eye, which can crawl along walls, has been found to have anatomical abilities similar to amphibians or reptiles. This discovery will allow biologists to better study how the process of transformation of prehistoric fish into terrestrial tetrapods took place.
A fish called the Taiwan blind eye, which can crawl along walls, has been found to have anatomical abilities similar to amphibians or reptiles. This discovery will allow biologists to better study how the process of transformation of prehistoric fish into terrestrial tetrapods took place.
5. Vertical landing of a space rocket
 Typically, spent rocket stages either fall into the ocean or burn up in the atmosphere. Now they can be used for subsequent projects. The launch process will be significantly faster and cheaper, and the time between launches will be reduced.
Typically, spent rocket stages either fall into the ocean or burn up in the atmosphere. Now they can be used for subsequent projects. The launch process will be significantly faster and cheaper, and the time between launches will be reduced.
4. Cybernetic implant
 A special chip implanted into the brain of a completely paralyzed man has restored his ability to move his fingers. It sends signals to a glove worn on the subject's hand, which contains electrical wires that stimulate certain muscles and cause the fingers to move.
A special chip implanted into the brain of a completely paralyzed man has restored his ability to move his fingers. It sends signals to a glove worn on the subject's hand, which contains electrical wires that stimulate certain muscles and cause the fingers to move.
3. Stem cells will help people after a stroke
 Scientists at Stanford University School of Medicine injected human stem cells into the brains of 18 volunteers who had suffered a stroke. All subjects showed improvement in mobility and general well-being.
Scientists at Stanford University School of Medicine injected human stem cells into the brains of 18 volunteers who had suffered a stroke. All subjects showed improvement in mobility and general well-being.
2. Carbon dioxide stones
 Icelandic scientists pumped carbon dioxide into volcanic rock. Thanks to this, the process of transforming basalt into carbonate minerals (later becoming limestone) took only 2 years, instead of hundreds and thousands of years. This discovery will make it possible to store carbon dioxide underground or use it for construction needs without releasing it into the atmosphere.
Icelandic scientists pumped carbon dioxide into volcanic rock. Thanks to this, the process of transforming basalt into carbonate minerals (later becoming limestone) took only 2 years, instead of hundreds and thousands of years. This discovery will make it possible to store carbon dioxide underground or use it for construction needs without releasing it into the atmosphere.
1. Another Moon
 NASA has discovered an asteroid that was captured by Earth's gravity. Now it is in its orbit, in fact being the second natural satellite of the planet.
NASA has discovered an asteroid that was captured by Earth's gravity. Now it is in its orbit, in fact being the second natural satellite of the planet.
List of unusual new gadgets of 2016 (CES)
10. Casio WSD-F10 smart watch
 This waterproof and very durable gadget works at a depth of up to 50 meters. The “brain” of the watch is the Android Wear OS. can synchronize with Android and iOS devices.
This waterproof and very durable gadget works at a depth of up to 50 meters. The “brain” of the watch is the Android Wear OS. can synchronize with Android and iOS devices.
9. Spherical drone
 The drone's blades may injure the owner or bystanders. To deal with this problem, FLEYE created a drone with a spherical design. Its blades are hidden, which means they are completely safe.
The drone's blades may injure the owner or bystanders. To deal with this problem, FLEYE created a drone with a spherical design. Its blades are hidden, which means they are completely safe.
8. Arke 3D printer
 Mcor has introduced a desktop device that allows you to print color 3D models using regular office paper. Print resolution is 4800x2400DPI.
Mcor has introduced a desktop device that allows you to print color 3D models using regular office paper. Print resolution is 4800x2400DPI.
7. Garmin Augmented Reality Device
 Varia Vision is a special display for cyclists placed on sunglasses. It not only informs you about your heart rate and blood pressure, but also helps you plan the optimal route.
Varia Vision is a special display for cyclists placed on sunglasses. It not only informs you about your heart rate and blood pressure, but also helps you plan the optimal route.
6. Origami drone
 The new paper product from POWERUP is controlled via Wi-Fi and can be equipped with an augmented reality helmet.
The new paper product from POWERUP is controlled via Wi-Fi and can be equipped with an augmented reality helmet.
5. Virtual reality helmet from HTC
 The HTC Vive Pre helmet allows you to physically move around objects in virtual space. The device claims: improved display brightness with greater detail and a built-in camera that allows the gadget to work in augmented reality mode.
The HTC Vive Pre helmet allows you to physically move around objects in virtual space. The device claims: improved display brightness with greater detail and a built-in camera that allows the gadget to work in augmented reality mode.
4. LG SIGNATURE G6V Super Slim OLED TV
 LG engineers integrated the OLED screen of the 65-inch TV model into 2.57 mm thick glass. Thanks to the stated color depth of 10 bits, the TV can display fantastically colorful images.
LG engineers integrated the OLED screen of the 65-inch TV model into 2.57 mm thick glass. Thanks to the stated color depth of 10 bits, the TV can display fantastically colorful images.
3. Solar Grill
 The GoSun grill has a unique design that directs sunlight towards a cylinder that can heat up to 290 degrees in 10 or 20 minutes (depending on model).
The GoSun grill has a unique design that directs sunlight towards a cylinder that can heat up to 290 degrees in 10 or 20 minutes (depending on model).
2. Passenger drone EHang 184
 The stylish new technology of 2016 will be able to carry one passenger for 23 minutes at a speed of 100 km/h. The destination is indicated on the tablet.
The stylish new technology of 2016 will be able to carry one passenger for 23 minutes at a speed of 100 km/h. The destination is indicated on the tablet.
1. Flexible screen for a smartphone from LG Display
 In the first position of the top 10 is a prototype of an 18-inch screen that can be folded like a sheet of paper. This type of futuristic display is promising for use in smartphones, TVs and tablets.
In the first position of the top 10 is a prototype of an 18-inch screen that can be folded like a sheet of paper. This type of futuristic display is promising for use in smartphones, TVs and tablets.
Illustration copyright Reuters
The new year has begun, and therefore the BBC Russian Service has chosen the 10 most striking scientific and technical achievements of the past 12 months.
1. The path to rapid genome editing has been opened
Illustration copyright SPL Image caption Human DNA can now be quickly edited, although no one yet knows what this might lead toA group of Chinese geneticists reported in a scientific publication earlier this year the first successful episode of editing the DNA of a human embryo using the CRISPR method.
The method of site-selective genome editing using an enzyme that recognizes the required sequence of a DNA strand based on the guidance of a complementary RNA guide promises revolutionary changes in the research and treatment of a number of diseases: from cancer and incurable viral diseases to hereditary genetic disorders such as sickle cell anemia and Down syndrome.
However, many biologists are calling for extreme caution in using this method of genetic engineering - for ethical reasons.
2. Autonomous power systems Powerwall
Illustration copyright Reuters Image caption The Powerwall battery system is already on sale starting at $3,000The head of the American company Tesla Motors, Elon Musk, said at a press conference that he is starting mass production of powerful lithium-ion Powerwall batteries that will be able to accumulate a large charge and gradually release it into the network as needed.
This system with a power of up to 10 kW/h is intended for use in private homes and small businesses.
The batteries can be charged from solar panels and other power sources.
The widespread use of this device has the potential to completely transform power distribution mechanisms in the future. The batteries are already being produced and are used in the famous Volta series electric vehicles.
3. There is liquid water on Mars
Illustration copyright SPL Image caption There is growing evidence that oceans existed on Mars 3.5 billion years ago. This water remains in the form of ice in the surface layers of the soil.Scientists exploring Mars have said that the dark streaks that appear on the planet's surface during the warmer months may be formed by periodic flows of liquid water.
NASA satellite images show characteristic streaks on the mountain slopes, similar to salt deposits.
As stated in a study conducted by scientists from the Georgia Institute of Technology led by astronomer Lujendra Oji and published in the journal Nature Geoscience, these data may mean that life may still exist on Mars in some form, since the presence of water increases the likelihood of the existence of primitive its forms - say, microbes.
4. Bionic lenses will end cataracts and myopia
Illustration copyright Getty Image caption New lenses allow you to quickly change the focal length of the eye and achieve unprecedented visual acuityCanadian optometrist Dr. Gareth Webb has invented a new system of bionic lenses that allows a person to achieve visual acuity three times greater than normal.
The Ocumetics Bionioc Lens system is implanted into the eye in a simple, painless surgical procedure that takes eight minutes.
A tiny biomechanical camera built into the lens allows you to change focal length faster than a healthy eye.
5. Neurons made of polymers
Image caption Polymer neurons easily take root in the brain and are not rejected by the bodySwedish researchers have created the world's first artificial neuron that can completely imitate the functions of a human brain cell, including its ability to transform chemical signals into electrical impulses and transmit them to other types of cells.
So far, the physical dimensions of such devices are tens of times greater than the parameters of real neurons in the human brain. However, as the leader of the research team, Agneta Richter-Dahlfors from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, said, reduction to the desired size is quite possible in the near future.
Transplanting such devices into the brain will radically change the treatment of neurological diseases such as Parkinson's syndrome and spinal cord injuries.
6. A step towards a working fusion reactor
Illustration copyright AP Image caption The Tri Alpha Energy reactor differs from the usual Tokamak design in the presence of proton acceleratorsCalifornian company Tri Alpha Energy, which few have heard of until now, has achieved major success in confining plasma with a temperature of 10 million degrees Celsius.
The company's experimental fusion facility uses not external magnets to confine plasma, as in Tokamaks, but beams of charged particles that are shot into the plasma and create a confining "cage" around it. The researchers managed to achieve a plasma confinement duration of 5 milliseconds, which is the largest breakthrough in the field of fusion research.
7. Fake memories can be transplanted
Illustration copyright SPL Image caption For the first time, it was possible to actively intervene in the functioning of the brain at the level of formation of associative memoryNeuroscientists in France were the first to implant fake memories into the brains of mice.
Using implanted electrodes to directly stimulate and record the activity of neurons, they created associative connections in the minds of sleeping animals that did not disappear upon awakening and influenced their behavior.
Karim Benchenan and his colleagues at the National Center for Scientific Research in Paris conducted experiments on 40 mice, implanting electrodes in the medial forebrain bundle, which controls emotions associated with food and reward, as well as in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, which contains at least three different types of cells , which encode information necessary for spatial orientation.
8. Found a way to make morphine from yeast
Illustration copyright Getty Image caption Morphine can now be produced industriallyScientists have developed a way to convert sugar into morphine and other similar painkillers using yeast.
Nowadays, painkillers are made from opium poppies.
Because heroin is also made from morphine, scientists warn the discovery will make it easier to make the drug at home.
9. Pluto's surface is riddled with deep grooves
Illustration copyright NASA Image caption The surface of Pluto turned out to be unlike the planets of the solar systemIn July of this year, the American space probe New Horizons reached the vicinity of the dwarf planet Pluto and its system of satellites, the largest of which is Charon. The photographs sent became a sensation in planetary science and revealed completely unexpected features of the planet’s topography and the mechanism of its formation.
Pluto has a rarefied atmosphere and even a change of seasons.
10. Three-parent fertilization is now a reality.
Illustration copyright SPL Image caption Mitochondrial genetic defects are relatively rare, but now there is an opportunity to end themThe British Parliament has approved a bill legalizing artificial insemination using genetic material from three parents.
Some women have defective mitochondrial genes, which can lead to the birth of children with serious genetic diseases - muscular dystrophy, heart defects, neurological disorders. The new method makes it possible to replace mitochondria in an egg using material obtained from a donor, and not just from natural parents.
MOSCOW, February 8 – RIA Novosti. The post-Soviet era is considered to be a time of deep crisis in domestic science, however, both in the 1990s and later, Russian scientists managed to obtain world-class scientific results.
In honor of Russian Science Day, the RIA Novosti agency conducted a large-scale survey of experts and compiled a list of the most important and most striking discoveries made by Russian scientists over the past 20 years. This list does not pretend to be complete and objective; it does not include many discoveries, but it gives an idea of the scale of what has been done in post-Soviet science.
Synthesis of superheavy elements will help discover new elements - scientistsExperiments on the synthesis of superheavy elements open up new “unexplored lands” for humanity and, ultimately, can lead to the production of long-lived superheavy elements, academician Yuri Oganesyan, scientific director of the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, told RIA Novosti.Super heavy elements
It was in the post-Soviet era that Russian scientists took the lead in the race for superheavy elements of the periodic table. From 2000 to 2010, physicists from the Flerov Laboratory at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna, Moscow Region, synthesized for the first time the six heaviest elements, with atomic numbers 113 to 118.
Two of them are already officially recognized by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and. The application for the discovery of elements 113, 115, 117 is currently being considered by IUPAC.
“It is possible that one of the new elements will be given the name “Moscovium,” Andrei Popeko, deputy director of Flerov’s laboratory, told RIA Novosti.
Exawatt lasers
Russia has created a technology that makes it possible to obtain the most powerful light radiation on Earth. In 2006, the PEARL (PEtawatt pARametric Laser) installation was built at the Nizhny Novgorod Institute of Applied Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, based on the technology of parametric amplification of light in nonlinear optical crystals. This installation produced a pulse with a power of 0.56 petawatts, which is hundreds of times greater than the power of all power plants on Earth.
Now the IPF plans to increase the power of PEARL to 10 petawatts. In addition, it is planned, which involves the creation of a laser with a power of up to 200 petawatts, and in the future - up to 1 exawatt.
Such laser systems will make it possible to study extreme physical processes. In addition, they can be used to initiate thermonuclear reactions in targets, and on their basis it is possible to create laser neutron sources with unique properties.

Super powerful magnetic fields
Physicists from the Russian nuclear center in Sarov, under the leadership of Alexander Pavlovsky, in the early 1990s developed a method for producing record-breaking powerful magnetic fields.
Using explosive magnetic-cumulative generators, where the blast wave “compressed” the magnetic field, they managed to obtain a field value of 28 megagauss. This value is an absolute record for an artificially produced magnetic field; it is hundreds of millions of times higher than the strength of the Earth’s magnetic field.
Using such magnetic fields, it is possible to study the behavior of matter under extreme conditions, in particular, the behavior of superconductors.
Oil and gas will not run out
The press and environmentalists regularly remind us that oil and gas reserves will soon - in 70-100 years - come to an end, this could lead to the collapse of modern civilization. However, scientists from the Russian Gubkin University of Oil and Gas claim that this is not so.
Through experiments and theoretical calculations, they proved that oil and gas can be formed not as a result of the decomposition of organic substances, as the generally accepted theory says, but in an abiogenic (non-biological) way. They found that in the upper mantle of the Earth, at depths of 100-150 kilometers, there are conditions for the synthesis of complex hydrocarbon systems.
“This fact allows us to talk about natural gas (at least) as a renewable and inexhaustible source of energy,” Professor Vladimir Kucherov from Gubkin University told RIA Novosti.

Lake Vostok
Russian scientists may have made the last major geographical discovery on Earth - the discovery of the subglacial Lake Vostok in Antarctica. In 1996, together with British colleagues, they discovered it using seismic sounding and radar observations.
Drilling a well at Vostok station allowed Russian scientists to obtain unique data on the climate on Earth over the past half a million years. They were able to determine how the temperature and CO2 concentration changed in the distant past.
In 2012, a Russian polar explorer managed for the first time to penetrate this relict lake, which had been isolated from the outside world for about a million years. Studying water samples from it may lead to and allow us to draw conclusions about the possibility of the existence of life beyond the Earth - for example, on Jupiter's moon Europa.
Mammoths - contemporaries of the ancient Greeks
Mammoths were contemporaries of the Cretan civilization and became extinct in historical times, and not in the Stone Age, as previously thought.
In 1993, Sergei Vartanyan and his colleagues discovered the remains of dwarf mammoths, whose height did not exceed 1.8 meters, on Wrangel Island, which, apparently, was the last refuge of this species.
Radiocarbon dating, carried out with the participation of specialists from the Faculty of Geography of St. Petersburg University, showed that mammoths lived on this island until 2000 BC. Until then, it was believed that the last mammoths lived on Taimyr 10 thousand years ago, but new data showed that mammoths existed during the Minoan culture in Crete, the construction of Stonehenge and the 11th dynasty of Egyptian pharaohs.
Third kind of people
The work of Siberian archaeologists under the leadership of Academician Anatoly Derevyanko made it possible to discover a new, third species of human beings.
Until now, scientists knew about two higher species of ancient people - Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals. However, in 2010, a study of DNA from the bones showed that 40 thousand years ago, a third species, called Denisovans, lived with them in Eurasia.
Methane and water on Mars
Although Russia has failed to conduct successful independent interplanetary missions in the post-Soviet period, Russian scientific instruments on American and European probes and ground-based observations have yielded unique data about other planets.
In particular, in 1999, Vladimir Krasnopolsky from MIPT and his colleagues, using an infrared spectrometer on the Hawaiian CFHT telescope, first detected absorption lines of methane on Mars. This discovery was a sensation, since on Earth the main source of methane in the atmosphere is living beings. These data were then confirmed by measurements from the European Mars Express probe. Although the Curiosity rover has not yet confirmed the presence of methane in the Martian atmosphere in these searches.
The Russian HEND instrument on board the Mars-Odyssey probe, created under the leadership of Igor Mitrofanov from the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, showed for the first time that there are huge reserves of subsurface water ice at the poles of Mars and even in mid-latitudes.
© State Astronomical Institute named after. PC. Sternberg Moscow State University M.V. Lomonosova/ Zhanna Rodionova
 10 February 2014, 14:29 Another pyramid discovered in Egypt and other scientific discoveries of the weekEvery Monday, the site's editors select the most unexpected scientific news from the past week. In this issue: why children forget what happened to them before the age of 7, who built the pyramid discovered in Egypt, how fertility depends on the level of education of women and much more.
10 February 2014, 14:29 Another pyramid discovered in Egypt and other scientific discoveries of the weekEvery Monday, the site's editors select the most unexpected scientific news from the past week. In this issue: why children forget what happened to them before the age of 7, who built the pyramid discovered in Egypt, how fertility depends on the level of education of women and much more.He began his work by comparing mythological motifs among the aborigines of Siberia and America, and then included in his research data on the cultures of almost all peoples of the world, which made it possible to paint an impressive picture of the primary settlement of people around the globe.
He proved that there are stable coincidences of certain mythological motifs in certain regions, which correlate with the ancient movements of primitive tribes, which is confirmed by archaeological and genetic data.
“Thus, for the first time in the history of science, we have a way to relatively accurately estimate the time of existence of the components of an oral tradition, which solves a number of central problems of folklore or, at least, gives researchers a guideline for subsequent research,” the professor told RIA Novosti Sergei Neklyudov from Russian State University for the Humanities.
Millennium Challenge
Russian mathematician Grigory Perelman proved the Poincaré conjecture in 2002, one of the seven “Millennium Problems” on the Clay Mathematics Institute's list. The hypothesis itself was formulated back in 1904, and its essence boils down to the fact that a three-dimensional object without through holes is topologically equivalent to a sphere.
Perelman was able to prove this hypothesis, but he received unprecedented popularity in the media when he received $1 million from the Clay Institute for this proof.