Despite the widespread introduction of circuit breakers, fuses are also used for protection against short circuits and overloads. In some houses and apartments they have not yet been replaced. But in electrical installations, fuses are used because of their advantages:
- they are cheap;
- the speed of disconnecting short circuits is higher than that of automatic machines;
- guaranteed disconnection of short circuits due to the absence of moving parts and assemblies;
- better arc extinction;
- the dimensions of three fuses are smaller than that of a circuit breaker for the same current;
- the dynamic resistance to short-circuit currents is limited only by the type of insulators used on which the fuses are installed.
Fuses are still used in household appliances and electronic products and will be used to protect them for a long time to come. This is due to its small size, reliability and low cost. Some devices use thermal relays instead, but in products where a short circuit is unlikely, the use of fuses is economically justified. Especially where their failure requires repair of the protected equipment in specialized workshops. The use of a thermal relay is more relevant in extension cords, where the likelihood of short circuits and overloads is higher, and the protection of the outlet to which it is connected does not provide a high-speed shutdown in abnormal operating modes.
Fuse models used in industrial electrical installations are equipped with replaceable fuse-links... The fuse body after a short circuit is not replaced if it has not received mechanical damage, and the insulation has not lost its properties under the influence of an electric arc. The use of inserts creates an additional advantage: replaceable elements designed for different rated currents are installed in the same housing. This makes it possible to unify places for the location of fuses in switchgears, and flexibly respond to changes in load power, changing the nominal current of the insert.
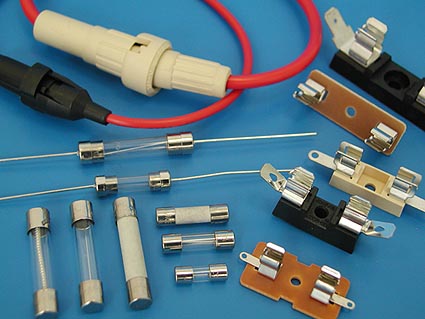
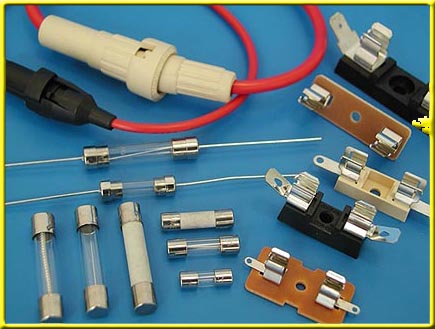
Fuses used in household equipment are also unified, but replacement of the insert in their housing is not provided. A fusible link is a wire made of a special material, located inside a glass or ceramic body in the form of a tube. The ends of the wire are soldered to metal caps along the edges of the tube, which simultaneously serve as leads for connecting the fuse to the electrical circuit. Such a fuse is completely replaced after operation.
The principle of the fuse
When an electric current is passed, the conductors heat up. Than more current or the smaller the conductor cross-section, the stronger the heating. Upon reaching a certain value, called the melting current, the conductor melts and collapses, thereby breaking the electrical circuit.
But this is not enough. At the moment of rupture, the short-circuit current may not be interrupted, but will continue to pass through the fuse through an electric arc arising from the ionization of the gas inside it. Three methods are used to extinguish it:
- Filling the cavity inside the fuse with a non-flammable substance. For this, quartz sand is used. By filling the fuse, it displaces air that can be ionized.
- Crushing the arc into parts due to the burnout of the insert simultaneously in several places.
- Application of spring loaded inserts. After they burn out, the spring is released and sharply increases the distance between the contacts, stretching the arc and forcing it to go out.
Fuse repair
Repair of fuses with replaceable inserts consists in replacing them with new ones, designed for the same current. The nominal current of the insert is indicated on its surface in those places that do not suffer from melting. In addition, the current of the fuse insert is indicated next to it on the device case, and in industrial facilities, a tag is additionally hung on the fuse case.
When cracks, soot, metallization from the action of an electric arc appear on the body, it is replaced. Any defect that can impair the arc suppression properties of the fuse will lead to problems when the next short circuit is disconnected: the case will melt, the arc will spread to adjacent contacts. The switchgear will shut down completely and be damaged.
Fuses in household appliances are completely replaceable. In fuses of the "plug" type, the fuse-link is replaced. But inserts for the required current are not always at hand. Sometimes it becomes necessary to temporarily repair the fuse, but at the same time ensure the trouble-free operation of the protected device.

Electricians have long solved this problem by installing instead of inserting a thin copper wire called a "bug". But when installing it, you need to take into account two main rules, the observance of which will preserve the safety of the repaired fuse.
2 basic rules for repairing a fuse
| Fuse rated current, A | Diameter of copper wire in insulation, mm |
| 0,25 | 0,02 |
| 0,50 | 0,03 |
| 1,0 | 0,05 |
| 3,0 | 0,09 |
| 5,0 | 0,16 |
| 10,0 | 0,25 |
| 15,0 | 0,33 |
| 20,0 | 0,40 |
| 25,0 | 0,46 |
| 30,0 | 0,52 |
| 35,0 | 0,58 |
| 40,0 | 0,63 |
| 45,0 | 0,68 |
| 50,0 | 0,73 |
Fuse (Fig. 1A) ("ceramic plug") is the simplest device for protecting electrical installations from overloads and short circuits. Plugs burn out during a short circuit in an electrical circuit or during prolonged overload.
The principle of operation of the fuse - inside the porcelain tube (1) of the fusible link ("fuse") there is a wire, which, when current flows through it, heats up. During an overload or short circuit, it burns out. In this case, the current circuit is broken. In the event of a short circuit, the fuse trips almost instantly, and in case of overloads, after a while.
All inserts are of the same length, but different diameters:
6A - 6 mm
10A - 8 mm
15A - 10 mm
20A - 12 mm
To protect against erroneous installation of an over-current replaceable fuse-link ("foolproof") at the bottom of the socket, there is a porcelain sleeve with a 6, 8, 10 or 12 mm hole above the central contact.
You can find out whether the fuse is whole or burnt out - you can use a multimeter or check with a simple lamp probe.
Threaded cork automatic machines (automatic cork) (Figure 1B) are screwed in like plugs. In case of overload and short circuits in the line, the machine turns it off. The chain is restored by pressing the button (2). The push-button switch (3) is used to disconnect the circuit.
Household machine (circuit breaker) (Fig. 1B) combines the functions of a fuse and a switch. After it is triggered, first move the toggle switch (4) to the "off" position, and then turn it on.
Of the listed devices, a conventional ceramic plug (Fig. 1A) with a fuse is the most reliable protection against overload and short-circuit in an electrical circuit. Interestingly, it is also inexpensive. Electromechanical fuses (Fig. 1B, 1B) have too large a "spread" in the operating current.
Attention:
Before turning on the "knocked-out" fuse, you first need to find out and eliminate the cause of its operation on the line.
If the contact is burnt in the plug, then it is not enough to replace only the fuse - you should completely replace the burnt plug with a new one.
Fuse selection
Main parameters:
- rated operating current at which the fuse element burns out and opens the circuit (6A, 10A, etc.) Usually, in everyday life, there is a ten-amp fuse or more. If the wiring is worn out - no more than ten amperes. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the high inrush currents of a piece of equipment - a refrigerator, a CRT monitor, etc.
- rated voltage (220 V);
- response time (fast, super fast)
To protect expensive household appliances, fuses are not enough - you need "Source uninterruptible power supply"(UPS) or at least a voltage stabilizer of the appropriate capacity.
rules:
Blown fuses should be replaced with the voltage disconnected.
All electrical circuits must be protected against short-circuit currents.
The fuse must be calibrated (that is, standard, in the factory).
Fuse calculation formula (up to 10A)
Summer residents often, when the "plug" burns out, temporarily put a home-made electric fuse "bug". Copper wire is selected by diameter, depending on required current operation (dependence is nonlinear). Too thick wire must be calibrated to a smaller diameter (see table)
For a thin copper wire with a diameter of 0.02 to 0.2 mm (without insulation thickness), the melting current (ampere) is calculated by the formula:
Ipl \u003d (d - 0.005) / 0.034
d is the diameter of the metal (copper) conductor in mm;
Table of the ratio of current strength to the cross-section of copper wire
Electrical fuse repair
- emergency repair electrical fuse. |
Attention: DO NOT USE in public networks - homemade uncalibrated fuse-links, as "bugs" instead of a factory fuse, so as not to violate electrical and fire safety rules. In amateur radio equipment, the use of homemade fuses is only in the case of sufficient inductance at the input (transformer or choke), if they are not there, install a "fast" electronic protection circuit. Food - autonomous. Attention: household appliances, after inserting any "self-made homemade product" into it, it may not be accepted for repair under warranty, in case of its breakdown. |
What should be done so that the electrical wiring does not burn out and there is no fire?
The simultaneous inclusion of several high-power electrical appliances in the power grid (especially in old houses with shabby electrical wiring) leads to its overload ("fuse is on") and can cause a fire;
- Do not leave switched on electrical appliances unattended;
- do not manufacture or use homemade heating devices, especially those of high power;
- switched on electric irons, electric stoves and other electric heating devices should be placed only on non-combustible and heat-insulating supports, and electric reflectors should not be left near objects that may catch fire;
- do not leave the turned on TV unattended if there are young children nearby;
- in order to avoid damage to the insulation and the occurrence of a short circuit, it is not allowed to paint over and whitewash cords and wires, hang anything on them or fix them to water pipes, to batteries heating system... Do not allow electrical wires to come into contact with telephone and radio transmission wires, radio and television antennas, tree branches and roofs of buildings. You can also not use telephone or radio lines as a conductor of electric current;
- it is unacceptable to place electrical wires in the space behind the suspended ceiling;
- you must not allow a large number of devices to be connected to one outlet or in one room;
- it is unacceptable to connect (twist) copper wires with aluminum ones, leave them bare or use unsuitable, old materials for insulation;
- only adults can turn on electric heaters. When leaving home, these devices must be turned off;
- heating devices can only be installed in non-combustible supports made of non-combustible materials of sufficient thickness;
- if the insulation of the electrical wiring in your apartment is damaged, dry or cracked, it must be urgently replaced. This also applies to old sockets, plugs.
According to statistics, the most common causes of fires in residential buildings are as follows:
- uncoupled cigarette butts, laid past the ashtrays, casually thrown on the floor or dropped from the hands of a person who is asleep on a bed while intoxicated;
- included electrical appliances, left unattended;
- faulty electrical wiring;
- children playing with matches;
- violation of the rules for the use of household gas appliances and gas cylinder installations of liquefied gases.
Overloading of networks (especially in old houses with dilapidated electrical wiring) occurs with the simultaneous use of such energy-intensive appliances as electric kettles, air conditioners, dishwashers and washing machines, heaters, as well as in violation of the rules of installation and operation of electrical wiring.
IN winter timeif pipes, central heating devices are thawed, they are often warmed with blowtorches, which leads to fires. It is recommended to use hot water or heated sand.
Typical power ratings for various devices are given in table 1. The exact values \u200b\u200bcan be found in the passport data. For most household appliances and tools, VA (volt-ampere) \u003d W (watt) can be read with sufficient accuracy.
Power consumption (watts) of household electrical appliances:
| Name | Power, W |
| Computer system unit | 200-500 |
| CRT monitor * | 200-300 |
| lCD monitor | 150-200 |
| Inkjet or dot matrix A4 printer | 100-200 |
| Laser printer A4 | 500-1000 |
| A4 scanner | 10-50 |
| Table electric lamp | 40-75 |
| Desktop unipolar air ionizer without fan | 2 - 5 |
| Aero. air ionizer bipolar with ventilator | 5 - 25 |
| Air conditioning * | 1000-3000 |
| Electric stove | 1000-5000 |
| Heater | 1000-2500 |
| Microwave oven * | 1500-2000 |
| Grill * | 1000-2000 |
| Oven | 1000-2000 |
| Electric kettle | 1000-2000 |
| Iron | 500-2000 |
| Toaster | 600-1500 |
| Coffee maker | 500-1500 |
| Hair dryer | 500-2000 |
| Vacuum cleaner * | 500-2000 |
| Compressor refrigerator * | 150-600 |
| TV (CRT, picture tube) * | 100-300 |
| Electric motors * | 500-3000 |
| Water pump (submersible) * | 500-1000 |
| Drill * | 300-1800 |
* The specified equipment has high starting (at the moment of switching on) currents. When calculating the total power, the rated power consumption must be multiplied by three (for the most powerful; for the rest, add the rated values \u200b\u200b"as is")
It is better to power expensive household appliances through a voltage stabilizer or UPS.
According to GOST, the voltage of the household power supply must be within 198: 231 V.
You can assess the magnitude and stability of the voltage in the network using devices or "by eye" - how the light is on (dimming or excessively bright glow). If the "light blinks" - a voltage stabilizer is needed.
Besides the current, there is also voltage ?!
If a voltage of several kilovolts is applied to a circuit with a conventional electrical fuse, then a spark breakdown is possible "past the wire" - to the body, to the "ground", etc. With a small electr. current - the fuse may not blow.
For an approximate calculation, at normal, normal air humidity: the breakdown voltage is 1 kilovolt per 1 millimeter of distance between the electrodes.
// So sparks on a sharp, angular electrode. On a ball, flat - the value of the breakdown voltage in air can be higher - up to 3 kV / mm.
The inverse problem: the length of the spark, arc \u003d 4 mm, which means U \u003d 4 kV (sufficient output voltage for the operation of the desktop air ionizer). The aeroionizer must be placed further from other electronics so that it does not burn out from the induction of static electricity ("static") from the radiating needles or the electromagnetic field from the high-voltage transformer windings.
Fuse characteristics:
- rated operating current at which the fuse element burns out and opens the circuit;
- Rated voltage;
- response time;
- voltage drop across the element;
- ambient temperature;
- size (second size - up to 25A, third standard size - up to 63A, etc.)
Rated current ... The most used standards are: UL 248-14, CSA 248.14 and IEC60127. They differ in response time of the fusible element from the flowing current.
Rated voltage - the maximum voltage at which the fuse is guaranteed to interrupt the emergency current, according to the selected rating.
Temperature at the surface (1 cm) of the fuse - must not exceed 70 ° C.
Response time... The main application of fuses is overcurrent protection. Different devices react differently to overcurrents. For some, the impact of a short-term current pulse with a large amplitude can be fatal, for others - a slight excess of the rated current, but for a long time interval. Therefore, fuses with different timing parameters are available: fast, ultra-fast and delayed fuses. A fast and ultra-fast fuse is used to protect devices from high amplitude transient surges in circuits where there are no turn-on surges or ripple currents (no transients). Ultrafast fuses are used to protect electrical devices on semiconductor elements. Time delay fuses are used in capacitive and inductive circuits where transient electr. processes when switching on and off, surges and current pulses (various electric motors, incandescent lamps, transformers, etc.)
Material used:
In many blocks and electronic devices, fuses are used to protect equipment in critical situationsat which electricity goes beyond its normal value. This method of protection is cheap and simple, but nevertheless quite reliable. The only drawback is that if the fuse thread blows out, it must be replaced with a new one.
And so, your electrical device or some kind of equipment stopped working, and you determined that you need to replace the fuse, but there is not always a new one in stock in order to quickly fix it this situation... What to do in this case? Do not run to the shops in search of the size you need and the required rating of the fuse-link ... Of course, not necessarily. In this case, you can do the resuscitation of the blown fuse, and how to do this, we will now figure it out.
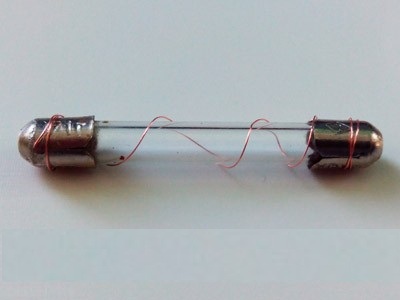
Make sure the fuse body is intact (glass or ceramics should not have cracks or other mechanical damage). One of the metal caps should have a stamp indicating the rated current of the fuse. This parameter depends on the material and diameter of the wire soldered between the caps. This small piece of wire can be made of copper, aluminum, steel or tin wire. It remains only to select the required wire diameter for the fusible link according to the table (as a rule, a copper wire is used), and replace the burnt-out hair in the bulb of the blown fuse.
The selection table for the material and diameter of the wire for a specific current is shown in the figure below:
To enlarge the table, click on the image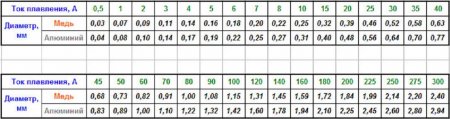
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that the rated current of the fuse-link, indicated on the cap, is the current that the fuse can withstand for a long time, and not the current at which the wire burns out. The destruction of a hair should occur in about 10 seconds, if the current exceeds the nominal 2 ... 2.5 times.
Probably, it is still worth writing how to correctly calculate the diameter and cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe wire, before soldering it in place of the burnt-out fuse hair. Of course, the best way to measure the diameter is with a micrometer, which gives you the most accurate data.

Finding the diameter of the wire using a regular ruler is less accurate. The essence of this method is to wind the wire turn to turn for a certain distance (the longer the winding, the more accurate the data will be). For example, the winding was 40 mm. Divide 40 by the number of turns, we get the approximate diameter of one core.
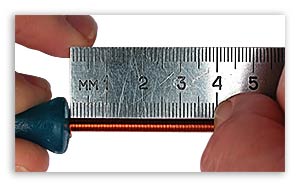
If you have a stranded wire available and you know its cross-section, then you can determine the diameter of one of its veins (wire), and use the table to estimate what current you can use this vein in the fuse. Let's give an example:
You have a stranded wire with a cross section of 1.5 mm, the number of veins in the wire is 19, divide 1.5 by 19, we get the cross section of one wire vein, i.e. in our case S \u003d 0.07894 mm, it remains to recalculate the value of the cross-section into diameter, for this we use the simplified formula:
We look at the table, if this vein is soldered into the fuse, then its rating will correspond to about 14 amperes.
Topic: fuse blown, what to do, how to restore it yourself.
Any fuse in an electrical circuit has a protective function. It is he who is the simplest, and at the same time, a fairly reliable way to ensure the safety of electrical, electronic circuits... Each fuse is rated for a specific tripping current. As soon as this current is exceeded, the fuse link will begin to melt, which will lead to its burnout and rupture of the circuit. This is what will make it possible to prevent excessive current from damaging other elements of the electrical circuit. The fuse is, as it were, originally designed to be the weakest link in this very circuit that breaks down first.
After burning, the fuse must be replaced with a new one. If the cause of the combustion was a normal voltage surge in the electrical network, and at the same time, apart from the fusible link, nothing else suffered, then after replacing the fuse with a known working device, it will work again. If the cause of the blown fuse is a specific malfunction in the circuit itself, then after replacing the fuse link it will burn out again. It is necessary to search and restore the circuit itself, and not to change constantly burnt out protective fuses.
It's good when you have a spare fuse at hand to replace a blown one. And if not, what to do? In this case, you can repair the fuse with your own hands, restoring its performance. Most in a simple way this can be done by inserting a new fuse wire and soldering the ends to the metal contacts of the fuse. New, factory-made fuses have a fusible conductor. In our case, we will get by with an ordinary thin copper wire, a fairly small diameter.
So, we will do the repair of the fuse like this - we take the burned out fusible link, in the sides on the metal contacts we make small holes with a thin drill. Next, we need a stranded wire that has fairly thin veins. I used a flesh-colored PVC insulated mounting wire (it contains just the wires of the required diameter). After I removed this very insulation from the wire, I pulled out one thin vein (its approximate section is about 0.1 mm). I inserted this vein into the holes made in the fuse. I ended up with a thin copper conductor inside the glass fuse body.
The ends with holes and a fusible conductor coming out from them were carefully soldered. That's it, the fuse is restored and ready to use again. Of course, it will not be as sensitive to excessive current as it was originally. But for most ordinary electrical circuits, with not very sensitive circuitry on the board, it is fine. Although, if it is possible, it is better to replace the burned-out fuse with a new one, purchased, designed for its operating (combustion) current.




