A device called a generator electric current, it is necessary to remember at least a little the law of electromagnetic induction. It is thanks to him that humanity freely enjoys all the benefits of civilization.
The principle of operation of a DC and AC generator using rotation
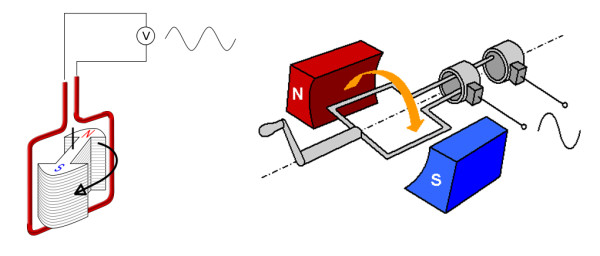
The law of electromagnetic induction states that in any closed conductor, the magnitude of the induced electromotive force is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux.
When the magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet rotates with a stable angular velocity around the axis, an electromotive force is excited in the frame. The vertical sides of the frame are active and the horizontal sides are inactive. This is determined by which sides cross the magnetic field lines in a particular circuit. In this case, in each of the sides, its own electromotive force is excited, which is directly proportional to the magnetic induction (B), side length (L) and the linear velocity of the magnetic field (v):
E1 \u003d B * L * v * sin (w * t)
E2 \u003d B * L * v * sin (w * t + π) \u003d - B * L * v * sin (w * t)
The resulting electromotive force is doubled, i.e.: E \u003d E1-E2 \u003d 2 * B * L * v * sin (w * t), because E1 and E2 act in accordance with each other.
The graphical display of the resulting electromotive force is a sinusoid. It - alternating current... To obtain d.C., it is necessary to bring the contacts from the working sides of the frame not to the slip rings, but to the half rings, the electric voltage will be rectified.
The principle of operation of a DC generator using chemical energy
Systems that convert chemical energy into electrical energy are called chemical current sources (CPS). It is primary and secondary. Primary HITs are not capable of recharging - these are batteries, secondary HITs are capable - these are batteries.
For the last 20 years, there has been a furor in the field of HIT. This refers to the creation of lithium-ion batteries. Their principle of operation is similar to a rocking chair: lithium ions move from cathode to anode, then from anode to cathode.
A chemical power source can only work when the following elements are present:
1) Electrodes (cathode and anode).
2) Electrolyte.
3) External circuit.
The potential difference between the electrodes is called the electromotive force. HIT generates electrical energy into the external circuit because with its help a redox process takes place, spaced apart. The oxidation of the reducing agent occurs at the negatively charged anode. Electrons are formed, which are transferred to the external circuit and directed to the positively charged cathode. This is where the oxidant is reduced with the help of these electrons. AT
The main purpose of the generator is to convert the energy of the carrier into electricity. The principle of operation of an electric generator is almost the same as that of your car running on fuel. The process seems extremely simple until you start to delve into the details.
A generator, like a car, has an engine that runs on one of the fossil fuels: gasoline, diesel fuel or gas. After fuel is injected into the cylinder, it starts to burn and turns into a rapidly expanding gaseous mixture that pushes the piston upward. When the piston moves, the crankshaft attached to it starts to move. The latter, in turn, rotates the drive shaft.
To rotate the crankshaft with more speed, multiple pistons can be used. Accordingly, you will receive high power at the exit. This parameter is usually marked in technical characteristics engine as the number of cylinders.
When the crankshaft rotates, it is time to consider the process of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is based on the physical law formulated by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry. The law reveals the essence of the question of how an electric generator works.
This law says: if a conductive loop rotates in a constant magnetic field, then a potential difference (electromotive force or voltage) appears in the loop. And when a voltage occurs in the circuit, an electric current begins to flow through it.
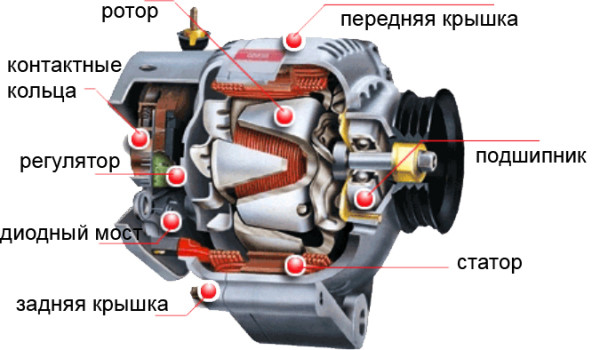
Main components of the generator
It consists of two fundamental elements: the stator and the rotor.
The stator is a fixed part of the device. It consists of three copper windings, each of which is laid around a core made in the form of a set of mild electrical steel plates. Mild steel is needed to enhance and concentrate the magnetic field in the stator windings.
The second part, rotating thanks to crankshaft, called a rotor or an anchor. It contains a mechanism for creating a magnetic field while rotating. For small generators, this mechanism consists of permanent magnets, and for large generators, it is a structure based on the principle of electromagnetic induction (such devices are also called brushless).
Voltage regulation
Another important element is the voltage regulator. It allows you to regulate the voltage and stabilize it when the speed and load change by controlling the excitation current.
This process occurs as follows: a part of the generator output voltage is supplied to the excitation winding through rectifiers that convert alternating current into direct current. Then, this direct current increases or decreases the overall magnetic field generated by the rotor. This adjustment improves productivity and required level output voltage.
However, the process takes some time, during which the generator output voltage reaches the required value. With a sharp increase in loads, voltage regulators will help to avoid voltage dips and ensure stable operation of the generator.
Generator cooling systems
There are two types of cooling systems: air and liquid.
System air cooling is an installation of a fan and a radiator that dissipates heat. The main element liquid cooling is a refrigerant that circulates through pipes, absorbing heat.
Correct and uninterrupted functioning of this system will help you avoid overheating of the electric generator and its subsequent failure. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly check the operation of the cooling system.
All of the above elements are essential for any electric generator. Often they come with the following equally important components: rechargeable batteries for starter and control panel for easy operation.
It would seem, why do you need to know the principle of operation, if you can simply replace the generator or send it for repair? From our point of view, there are at least two reasons for this.
First, to correctly determine which part of the "circuit" is faulty - the generator itself or something else. Maybe it's not about him, but about the unreliable fastening of the terminals and the like?
Secondly, knowing the structure and operation of this or that product, it is often possible to carry out repairs on your own, without wasting time looking for "specialists" or a store.
It seems to us that such an introduction will cause some interest in this article, especially since we will not "load" the reader with theory mixed with numerous formulas, but consider the issue in a simplified form, based on what may be useful to us in practice.

This name - - means any device that converts some other type of it into electrical energy (thermal, mechanical, and so on). But more often most of us, especially owners of cars and suburban real estate, are faced with products in which the "primary" is mechanical energy.
Almost everyone has seen the models of electric generators shown in the photo, and many have them (individually or as part of other devices) in personal property.

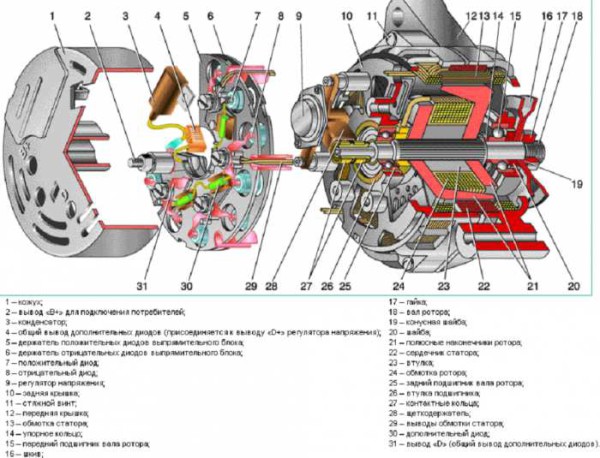
Essential elements
- Stator (magnet system enclosed in a molded case).
- Rotor (system of conductors wound in a special way).
- Current collector - a collector and brushes (graphite), which “remove” the voltage from it, then entering the electrical circuit (for example, a car). By the way, some models lack brushes.
Such devices use the self-induction effect. In simple terms, it is the occurrence of an electric current in a conductor located in an EM rotating field. Although there are other options - for example, the magnetic system is stationary, and the "frame" itself rotates. AT car generators Both the stator and the rotor have their own windings.
It is enough to look at the pictures below, and not only school years are immediately remembered, but also something else that was heard at one time in physics lessons.
In practice, it is done like this. The stationary part of the product is the stator, which is rigidly fixed. Inside it is a rotor, which is driven by some kind of engine. It can be connected to it either "rigidly" (sit on its shaft), or by means of a belt drive.
The applied engineering solution largely depends on what kind of current needs to be obtained from the generator - alternating (as in autonomous power supply systems for residential or industrial facilities) or constant.
What do we gain from the general knowledge gained about the principle of operation of an electric generator, what is it for?
 Activities and types of maintenance of diesel generators - list of works and tips
Activities and types of maintenance of diesel generators - list of works and tips