The cooling system of a car engine requires increased attention both in the warm season and in winter period... Therefore, correct and timely maintenance of the cooling system will help you get rid of many problems with the machine, most often due to non-observance of basic rules.
The car cooling system has a rather complex structure, reliable work which is possible only if all of its components and assemblies are in good working order. Ideally, system maintenance should be limited to just two points:
- Flushing - instructions for flushing the engine cooling system;
- Replacing the coolant - instructions for replacing antifreeze.
But ideal conditions do not exist, therefore, during the operation of the car, it is important to monitor the tightness of the cooling system and what you pour into it. In this article, we will tell you what to look for when servicing the engine cooling system to prevent malfunctions.
For details on how the engine cooling system works in a car and about the features of its maintenance, see the video at the bottom of the page.

First, let's remember what is in your cooling system? Not so long ago, it was quite common to find cars with water in the engine cooling system instead of antifreeze. Fortunately, the use of water as a coolant is rather the exception to the rule these days. It is usually used in emergency situations, when something needs to be poured into the system, but there is no antifreeze at hand.
If we compare the characteristics of water and a special coolant (antifreeze), then the latter has a lot of advantages - a higher boiling point and a low freezing point, and the presence of softening and anti-corrosion additives in the composition that prevent the formation of scale and rust in the engine cooling system.
We have decided on this question - no water in the engine cooling system! But it should be borne in mind that the durability of the system largely depends on the quality of the coolant. You should not buy the first available canister labeled "Antifreeze" or "Antifreeze", you need to give preference only to products from reliable manufacturers with all the necessary certificates.
Most counterfeit fluids contain corrosive acids, which over time corrode not only the parts of the cooling system, but also lead to the appearance of "cavities" even in the cylinder head! Therefore, we do not advise you to save on antifreeze.
We wrote in great detail about the types of car coolants, their differences from each other, and how to choose antifreeze for your car in this article, we strongly recommend that you familiarize yourself!
Also, one of the important criteria for the quality of the coolant is the presence of special fluorescent additives in its composition, which help to detect leaks in the engine cooling system. Since the system must be sealed, leaks in it are unacceptable.
Checking the cooling system for leaks
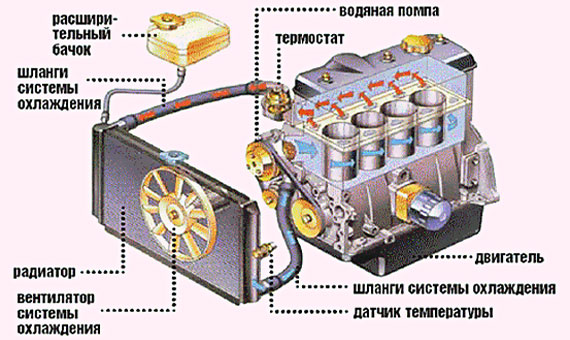
Checking the engine cooling system for leaks is a very important stage in its maintenance. The fact is that in a sealed system, antifreeze boils at a temperature of 130 ° C, and under normal conditions it boils at only 108 ° C. Therefore, the slightest crack, for example, in the cooling radiator, rubber hose or in the expansion tank, breaks the tightness and the engine boils.
To facilitate the search for microcracks in the engine cooling system, special fluorescent additives, which are part of modern antifreezes, help - thanks to them, it glows in the rays of an ultraviolet lamp.
But, unfortunately, not every motorist has such a lamp. Therefore, in the process Maintenance engine cooling systems, we recommend adhering to a few simple rules:
- To check the liquid level on the expansion tank, there are MIN marks and MAX. With a cold engine, the antifreeze level should be between these two marks.
- If the coolant level in the expansion tank is constantly decreasing, then this indicates a leak, that is, a violation of the tightness of the engine cooling system.
- Carefully inspect your radiator and pipes for leaks and smudges, if necessary tighten the connecting clamps and make sure that the radiator cap is closed all the way.
The presence of air in car system cooling (so-called "air locks") can also disrupt its operation. Below we will show you the easiest way, how to expel air from the engine cooling system.
The presence of air in the cooling system is checked as follows:
- Open the lid expansion tank,
- Turn on the heating of the passenger compartment full power and let the motor run on idle two or three minutes,
- If there is air in the cooling system, bubbles will appear in the expansion tank.
In order to remove air from the engine cooling system, the car must be placed at an incline, so that the "front" is slightly "lifted" to the top. Further, the sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Open the radiator cap and start the car.
- Turn on the stove and let the engine run for a few minutes to allow air to escape from the system.
- After that, the motor can be turned off and the radiator cap closed.
Now let's look at a few more nuances that you should pay attention to when servicing the engine cooling system to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions or to eliminate them.
What to look for when servicing the engine cooling system

To prevent malfunctions of the engine cooling system, it is necessary to regularly perform the following maintenance operations:
- Checking the density of the coolant... The density of the antifreeze is checked with a hydrometer. At higher gravity, dilute your liquid with distilled water, and at a lower density, dilute with a similar coolant.
- Tension drive belt ... One of the most common causes of overheating in a car engine (especially with a mechanically driven fan) is a loose drive belt. Belt slip reduces pump performance and, consequently, impeller speed.
- Cleaning the engine cooling system... Also, do not forget to check the external condition of the motor and radiator. Both the radiator and engine need to be cleaned regularly as dirt and debris interferes with proper engine cooling. Often, the radiator is clogged with dirt, dust, poplar fluff and other filth. All this debris can be easily removed with a strong jet of water or a powerful vacuum cleaner. Engine oil spills and dust adhering to them should also be washed off regularly.
- Checking the thermostat... An important element of the cooling system is the thermostat, which maintains the optimal operating temperature of the motor, as well as quick warm-up engine immediately after starting. We wrote in detail about how the car thermostat works and the methods of its diagnostics in the article about the device and the principle of operation of the car thermostat.
- Engine cooling fan... Another element that requires attention when caring for the engine cooling system is the fan. Most modern cars installed electric fans cooling, which are controlled by a thermoelectric sensor screwed into the radiator. When the set temperature is reached, the sensor contacts are closed, and the fan starts to work, cooling the radiator surface.
If the fan does not turn on when the engine heats up, then the reason for this may lie in the temperature sensor. The performance of the sensor is determined very simply, for this you just need to close its contacts:
- if the fan is running, then the sensor is faulty,
- if not, the reason is either in the fan motor or in the electrical circuit of its power supply.
Video about the features of servicing the engine cooling system
The cooling system of each car is a rather complex device with many different components that make up it. And the most common malfunction is an airlock. This article will focus specifically on this breakdown, the causes of its occurrence, consequences, remedies, and also about preventive actions.
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the cooling system as carefully as for the most important car systems. Photo: lr-club.com
What is an airlock and symptoms of manifestation
Some novice motorists have often heard this expression "airlock", but not everyone knows what it is and whether it is dangerous for a car's operation. An airlock is the ingress of air into the coolant (coolant) circulation system. As a result of the occurrence of such a malfunction, the correct circulation of coolant through the system will be disrupted, which in the future can lead to expensive repairs.
The main symptoms of airiness manifestation are as follows:
- Lack of heat inside the car. Due to the fact that air has entered the cooling system, there is no coolant supply to the heater radiator, and, therefore, there is no heat.
- Overheating of the engine internal combustion(ICE). If the system is airy, then the coolant cannot move calmly and, as a result, the engine overheats. This can be determined by the temperature indicator, which is located on the dashboard;
- Decreased engine power.
If such defects are found, all components included in the system should be inspected.
Now it is worth considering the reasons why this problem occurs.
Reasons for airing the cooling system
There are many reasons why air can enter the cooling system, but it is worth considering the most common:
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket (cylinder head). If cylinder head gasket damaged, then a coolant leak is possible, this will manifest itself as follows: seething in the expansion tank, liquid entering the oil pan, as well as white steam from the muffler.
- Depressurization of the water pump (pump). In the event of a depressurization of the pump, it can pick up air and then an air lock forms.
- Depressurization of elements of the cooling system. Air can enter the system through a breach of the seal at the joints of the pipes, fittings and pipes. While coolant will pass through the pipe or pipe, air may be sucked in from the outside at the place of damage.
- Broken expansion tank cap.
The expansion tank plug works like a valve and relieves excess pressure. In the event of a breakdown, the reverse process occurs and it begins to pump air into the system.
- Damage to the radiator.
Another common cause of air congestion is the ingress of air into the system when replacing or refilling coolant.
What can air in the cooling system lead to?

The consequences can be different, from minor to critical, everything will depend on the moment at which the motorist discovered the malfunction. Photo: mail.ru
Of the minor consequences, the following can be noted:
- failure of various sensors. As a result of the breakdown of the sensors, incorrect data will be received about the operation of the car;
- partial or complete absence heat in the car;
- increased fuel consumption;
- increased wear of internal combustion engine parts.
If the air in the cooling system is not detected and eliminated in time, this can lead to damage to the internal combustion engine.
Materials and liquids expand when heated, if there is no proper cooling, this can lead to a modification of the engine components, and as a result to the death of the motor. And then to expensive and time-consuming repairs. Now it is necessary to consider the ways in which the airlock is eliminated.
Air Lock Removal Methods
There are several ways in which an air lock in the cooling system is eliminated. All of them are quite simple and there is no need to visit a service station.
The first way looks like this:
- the plastic protection is removed;
- then use a screwdriver to loosen the clamp fastening and remove the upper or lower branch pipe throttle;
- then the cap of the expansion tank is unscrewed and a clean rag is placed on the neck;
- now you need to blow into the expansion tank with all your strength, the procedures should be performed until coolant flows from the removed pipe;
- put the pipe back in place and tighten the clamp, as well as put the protection in place.
Second way:
- drive the front wheels onto a rise or overpass in such a way that the radiator cap becomes the top point in the cooling system;
- unscrew the caps from the expansion tank and the cooling radiator;
- start the engine and bring it to an operating temperature of 90 degrees;
- then it should be gassed and gradually add coolant to the expansion tank. Top up until no more bubbles appear in the tank.
Third way.
- it is necessary to bring the engine to an operating temperature of 90 degrees and turn off the engine;
- now, using a screwdriver, the clamp of the throttle valve pipe is loosened, and the pipe itself is directly removed;
- then you should wait until all the air that has entered the system comes out of the pipe, as soon as the coolant runs, you should quickly put it in place.
In these ways, you can get rid of the airlock with your own hands. It is worth noting that of all the methods, the first one is 100% effective.
Also, if you follow some simple rules, which will be discussed below, you can avoid the occurrence of malfunctions with the cooling system.
You can find a video instruction on bleeding the cooling system here:
Which will reduce the risk of an airlock
If you adhere to the rules for operating the car, then you can significantly reduce the risk of an airlock in the car. These recommendations look like this:
- compliance with regulations service book on the passage of technical maintenance (MOT);
- checking the coolant level at least once a month;
- fill only with recommended and high quality coolant. Very often, if a low-quality coolant is used, then the system is airing.
Outcome
It's time to take stock. The cooling system in each vehicle plays a major role in providing the required cooling and maintaining the required internal combustion engine temperature, and is also responsible for heating the passenger compartment. If you carry out scheduled maintenance on time and monitor the coolant level, then there will be no problems with the engine. After all, if you do not notice and eliminate the airing of the system in time, then this can lead to serious problems, in some cases to overhaul ICE.
Where does the air in the cooling system come from if all the clamps are well tightened, the level of antifreeze is always normal, there are no leaks, the thermostat and pump are working perfectly.
I think the reason is that a steam outlet pipe is made from the radiator into the expander reservoir, and that's where an air lock is formed. The radiator cools down faster and warm antifreeze from the expansion tank begins to evaporate air into the system. It is necessary to drive the air downward by squeezing the antifreeze in the tank of forces, but it is very likely that it is easy to drive the air back into the radiator under pressure and create bubbles in the upper branch pipes of the system.
How is the airing of cleaning and diagnostic facilities during the normal operation of a car with normal level Coolant, tightly tightened clamps, sealed radiators and a serviceable RB plug?
Let's take a look at the drawing of the SOD in photo 2. The steam hose no. 6 is never completely filled with coolant. If it were transparent, then we would see in the process ICE operation that inside it areas with liquid alternate with areas of air. The surface tension prevents the liquid from settling at a certain level. In addition, in our RB, the “MAX” level mark is about 60mm above the engine radiator steam outlet no. 11. When the internal combustion engine is cooled, and therefore the coolant poured into it, atmospheric air is drawn into the upper part of the radiator, from where it enters the thermostat through the supply hose No. 9, which has a slight slope. In the morning we turn on the internal combustion engine, the pump of which, by the pressure of the coolant, entrains the trapped air into the heater radiator through the supply hose No. 2 and into the internal combustion engine through the hose of the supply pipe No. 3. But do not think that the very next day in the morning you will get a problem with ODS. No. This happens gradually, day after day, and depends on the outside temperature. First of all, we hear different sounds from under the dashboard. Waterfall, gurgling, overflowing water, murmuring ... In the cold season, this is added to a decrease in the heat output of the heater radiator. It's cold in the cabin. And only when the temperature of the internal combustion engine "creeps" along the instrument board to the red zone, and the fans of the internal combustion engine radiator do not cease for a long time, we begin to scratch the back of our head. Worst of all, if we find out about the problem with SOD by the clubs of steam from under the hood.
From this situation, I found such a way out - it is necessary for the steam outlet to sink in antifreeze at the bottom of the expander tank. I took the system from a medical dropper, stuffed the needle with a tube from the dropper into the expander branch pipe, then put this branch pipe with the tube inside from the dropper back onto the tank and tightened it up. That's it, now back pressure from above into the system through the radiator cannot be created in any way, there is no return air to the radiator.
How to make a water seal?
photo 3
We cut off somewhere 15-20 cm of the tube from the dropper. We put on a needle tip on one end. We tighten the tube on the fitting from the needle as much as possible. The needle itself can be broken off initially. Next, we push this entire structure into the expansion tank fitting, and cut off the excess part of the needle fitting, as shown in the photo. In order for the dropper hose to be pushed into a 90-degree angle in the Republic of Belarus, you need to cut the end of the tube to a bevel - this way it will be easier to push through there. Next, we put on the RB branch pipe and clamp it. That's it, the water seal is made, there is no return air from the RB to the radiator.




