The rechargeable battery is one of the main devices of a car, which tends to wear out during operation. Therefore, from time to time, car owners have to change the battery due to the fact that it cannot perform its functions. You can find out more about how to restore a car battery at home below.
[Hide]
Recovery by low current
How to bring back to life and revive your car battery? This device provides continuous transmission of current to power electrical equipment vehicle... Accordingly, without this device normal work devices will be impossible, especially since over time the battery can no longer hold the nominal charge required for power supply. Not all batteries that work poorly need to be thrown away - you can try to reanimate the old battery. This will avoid unexpected financial costs.
Device and designation of the components of the battery structure
If we talk about acid-base batteries, then the structure consists of several positive and negative lead plates in sulfuric acid. Today, devices of this type are the most common among cars used in the countries of the former USSR. Despite its prevalence, battery life is lower.
Do-it-yourself car battery restoration can be carried out using the technology of repeated recharging. In this case, a small current must be used. The charging procedure with the charger-recovery device must be carried out intermittently. Starting from the first charging of the device to the last, the voltage level that is present in the battery will gradually increase. As a result, the device should stop discharging.
The charger and recovery device must work with pauses, this will allow the potentials of the electrodes, which are in the plates, to equalize. The recovery procedure itself is safe for electrodes. The use of a charging recovery device with pauses will ensure the transition of the densest electrolyte from the plates to the space between the electrodes.
 Unscrewing the battery caps
Unscrewing the battery caps As a result of the partial discharge technique, the density of the electrolyte is increased. The owner of the car is required to wait until the moment at which the voltage corresponds to 2.5 volts, and the density parameter will correspond to the nominal one. And in this case, we must not forget that the car battery needs a break, so the charging recovery device must be periodically disconnected. For full resuscitation, the cyclic recovery procedure must be repeated 8 times. It should be borne in mind that the indicator of the current used should be 10 times less than the capacity of the charged battery.
Electrolyte replacement
It is possible to restore the battery by replacing the electrolyte; this method has proven its effectiveness in practice. To replace the electrolyte, the liquid from the structure must be completely drained, after which the system must be flushed with warm or hot water. After rinsing, you will need a few tablespoons of regular baking soda - 3 tablespoons are diluted with 100 ml of water, while it is advisable to use a distillate.
 Pouring soda solution into the battery
Pouring soda solution into the battery The mixed solution must be boiled and poured into the structure instead of the drained electrolyte, then leave the battery for 20-30 minutes. Then drain the liquid from the device, and repeat the procedure three more times. After the last cycle, rinse the structure again with hot water, preferably several times.
The method is relevant for many types of batteries. After the structure is washed, you need to pour a new electrolyte into it and put the battery on charge. The charger must be turned on for 24 hours.
Then produced cyclic charging the device - 6 hours daily for 10 days. At the same time, we note that the charger itself should have such properties - the voltage parameter should be no more than 16 volts and not less than 14. As for the current strength, the indicator should be no more than 10 amperes.
Reverse charging
How to recover car battery? To do this, you can use the method reverse charging... It is quite possible to carry out the procedure at home, but this will require a sufficiently powerful power source, for example, a welding machine. The device that you will use must have a voltage of at least 20 volts, while its current must be at least 80 amperes. After removing the equipment, it is necessary to unscrew the plugs on top of the battery structure and perform the reverse charging procedure.
To accomplish this task, connect the positive output of the charging equipment to the negative terminal of the battery. The negative output of the charger is connected to the positive. If everything is done correctly, the procedure will increase the battery life by several years.
Note that the car battery may boil while charging, so don't worry. The device should be charged for exactly 30 minutes, no more and no less. After that, the electrolyte must be drained from the structure, and the device itself must be rinsed with hot water. When all the steps are completed, a new electrolyte can be poured into the structure. Upon completion of these actions, the battery will need to be connected to a conventional charger (the current parameter of which should not exceed 15 amperes) and charge the device for the next 24 hours.
Charge recovery in distilled water
If you are not sure how to restore the battery and which method to use for this, we offer another option. Using it, you can restore the device to work in less than 60 minutes. If the car battery is completely discharged, it will need to be charged in advance. The old electrolyte must be completely drained from the charged battery by first unscrewing the plugs on the cover, after which the structure can be rinsed with water. As in the previous cases, it is better to use a distillate for this.
After the battery is charged and flushed, a special ammonia-type Trilon B solution should be poured into the structure. The solution contains 2% trilon and 5% ammonia. With the help of a liquid, a desulfation procedure is carried out, which takes no more than an hour. As the battery recovers, it will be possible to notice the release of gas from its structure, which is also accompanied by minor splashes that will appear on the surface. These gases are harmless to the body and human health, but it is better to place the battery in a ventilated room. When the system stops emitting gas, this will indicate the termination of the desulfation process.
When the steps are completed, the structure must be rinsed with distilled water - rinsing is carried out several times. After flushing, the device must be filled with electrolyte of the appropriate density. The device needs to be charged again and after that it can be considered restored. In general, the procedure for charging and restoring the battery's performance is not complicated; even an inexperienced car enthusiast can handle it.
Not all modern batteries are recoverable. Sometimes the device can be reanimated for a day, several days or for a week, and sometimes restoration allows the battery to work for several years. Much depends on how the battery was used, in what conditions, how many electrical appliances were connected to it throughout the entire service life. The conditions of use play an important role - if the device was often used in a discharged state, it is likely that it will not be possible to restore it.
Need to clarify the point on use charger... The charger must be in good working order, otherwise its use will damage the battery. Our resource has already written about and the use of special chargers. You can find detailed recommendations on this issue in.
New or stored dry batteries are filled with electrolyte in such a way that its level after a two-hour impregnation is 5-12 mm higher than the plates.
Once installed normal level electrolyte, the batteries are switched on to a charge, which is produced in two stages: first, with a current equal to Q: 4, for 6 hours, and then with a current equal to Q: 8, during the same time, where Q is the capacity in ampere-hours. The battery is discharged by the current of the second stage for 4 hours. The indicated mode is performed for 2-3 cycles, after which the batteries can be put into operation.
Batteries that have been stored with electrolyte for more than one year are put into operation without changing the electrolyte; in case of longer storage, the latter must be replaced. The said batteries are put into operation in the described manner.
With a normal charge during operation, the battery is reported to at least 150% of its nominal capacity. The temperature during charging should not exceed 30 ° C for caustic potassium, 40 ° C for caustic soda and 45 ° C for a composite electrolyte. If the specified temperature is exceeded, it is necessary to interrupt the charging process and allow the battery to cool down. The battery is charged at temperatures below -10 ° C (up to -30 ° C) with normal current for 7 hours. low temperatures Before charging, the battery must be insulated by covering it with felt or tarpaulin. Charging is usually done with the battery box lids open and the plugs turned out.
Once a month or after 10-12 cycles, the batteries are charged according to a mode similar to the actuation mode.
Systematic undercharging destroys the battery. Boost charges are also undesirable and should only be used when absolutely necessary. Such charges are produced according to the mode of current Q: 2 for 2.5 hours and current Q: 4 for 2 hours. The discharge of an alkaline battery during operation can be carried out up to the final voltage: with an 8-hour and longer discharge mode - up to 1, 1 V, with a 5-hour discharge mode - not less than up to 0.8 V, and finally, with a 1-hour discharge mode - not less than 0.5 V.
Every 50-60 cycles, but at least once a year, it is recommended to carry out control electrical tests checking the capacity of each battery in the battery. Cells giving less than 80% of the rated capacity must be replaced with new ones.
During operation, before each charge, check and, if necessary, correct the electrolyte level, using distilled or rainwater for this purpose.
If the battery operates all year round under constant temperature conditions, the compound electrolyte is changed every 100 cycles, but not less than once a year. It is possible to change the electrolyte earlier than the specified period with a noticeable decrease in capacity, if it is not possible to restore it by overcharging.
When transferring to long-term (more than 1 year) storage, the battery in operation is discharged to 1.0 V with current according to the normal 8-hour mode, the electrolyte is poured out and, without washing the battery, it is tightly closed with a plug.
Batteries, periodically (for a period from 2 months to 1 year) inactive, can be stored with electrolyte in a discharged or semi-discharged state. Unused batteries are pre-stored at the factory. Batteries and batteries must be stored in a clean, dry, ventilated room with a temperature of 15 to 25 ° C.
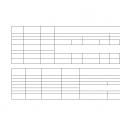
The main malfunctions of alkaline batteries and how to eliminate them are shown in table. 26.
Table 26
The main malfunctions of alkaline batteries
|
Cause of malfunction |
|
Malfunction |
Troubleshooting method
Loss of capacity
Increased self-discharge
No voltage to the battery
Rapid formation of creeping salts
The battery does not work at low temperatures; freezing of electrolyte
Lowering capacity in hot weather
Long-term operation with an electrolyte from caustic potassium or caustic yatra; accumulation of carbonic salts
Low electrolyte levels; exposure of part of the plates
Systematic no - additional charge
Short-circuits Current leakage Presence of harmful impurities in the electrolyte
Short circuits
Leakage current
Impurities in the electrolyte Lack of contact in the connections between the battery cells
Lack of electrolyte in one of the cells
Breakage of the pin connecting the plates with the pole clip
Poor Vaseline lubrication, too high a level or high electrolyte density, weakness of the glands at the electrode bolts
Defective cover welding
Low density
Electrolyte
Excess potassium carbonate in the electrolyte
High temperature charge
Electrolyte ns potassium hydroxide solution
Change electrolyte
Check the integrity of the plug and sealing rings
Bring the electrolyte level to normal, produce an enhanced charge
Produce one or more Empowered Charges
Remove debris between the elements, remove dust and dirt and tidy up the insulators
Inspect and clean batteries
Tidy up the insulators Change the electrolyte Find the place of damage and restore contact
Element electr0-
Spot element
Refresh the lubricant with Vaseline
Correct the density of the electrolyte and bring its level to normal
Tighten the electrode bolts
Take the battery to a repair shop
Switch to new electrolyte Change electrolyte
Charge at night and as cool as possible
Replace the electrolyte with a composite one, and in its absence - with caustic soda
|
ALKALINE BATTERIES WITH SILVER OXIDE ELECTRODE |
The technological process of repairing alkaline batteries begins with removing the batteries from the car, after which they go to the battery repair section. Battery repair is carried out with and without opening the can.
Repair of batteries without opening the can is carried out with partial disassembly: nuts are screwed off the bores, jumpers are removed and rubber covers... Banks and lintels are cleaned of dirt and grease by washing in a drum-type machine with 1% caustic soda solution heated to a temperature of 60-80 C. After rinsing with clean water, the parts are sorted, nuts with crumpled edges and faulty threads are discarded, deformed lintels are straightened, lintels with cracks or damaged nickel plating is replaced. Suitable parts are transferred to the battery assembly position.
Rubber covers are washed outside and inside with hot water, into which a little sulfuric acid or old acidic electrolyte is added to neutralize the alkaline electrolyte remaining on the surface. After neutralization and washing with running water, the covers are tested on a special press with a water pressure of 0.1 MPa. Crimping the covers can be replaced by checking the dielectric strength of the rubber alternating current... The covers that have passed the test are dried in a special chamber.
Covers with through abrasions and small punctures during depot repairs are allowed to be vulcanized with raw rubber or restored by setting glass fabric linings on the GEN-150V adhesive using a special technology. During overhaul rubber covers with defects of this kind must be replaced with whole ones.
In parallel with the above works, the batteries themselves are being repaired. First, the electrolyte is poured out of them, and then each jar is washed outside and inside. The drained electrolyte is collected in a regeneration tank.
Mechanized washing of alkaline batteries can be carried out in a special washing machine with two washing chambers equipped with exhaust ventilation. A cart with a swivel basket, in which batteries are installed, is rolled into each chamber. At the beginning, the basket is turned and the electrolyte is drained from the batteries and then they are poured with water heated to a temperature of 60-70 ° C, it is impossible to use hotter water - since the separators between the plates made of vinyl plastic can soften and deform. After that, the basket shaft clings to the drive motor clutch and the basket is shaken, the batteries are rinsed and the water is drained. After a set time interval, a new cycle begins. The washed batteries are examined, places with traces of corrosion are cleaned, wiped with napkins dipped in 10% phosphoric acid. The plates are inspected, defective springs and rubber seals, which do not ensure a tight closure of the battery neck, are replaced. After repair, dry batteries are inserted into rubber cases and placed on racks for electrolyte filling and charging. After cleaning, the cans are painted outside by dipping with varnish. Other materials can be used to provide reliable protection metal from corrosion. The outer cover is not painted, but is filled with hot graphite or, in extreme cases, covered with a layer of technical petroleum jelly.
The outer painting of the cans can be omitted if they protective coating no defects or traces of corrosion. It is imperative to fill the lid with paraffin in any case, since this prevents current leakage along the lid if electrolyte is accidentally spilled on it when filling the battery or charging it.
With an increased carbonate content, the batteries are poured with alkalized water heated to a temperature of 100 ° C and kept for 16-290 hours, periodically pouring out the water and shaking each battery. The same washing is carried out when replacing the potassium electrolyte with sodium electrolyte and vice versa.
The capacity of nickel-iron batteries is restored by treating them with sodium sulfide. This process improves the state of negative iron electrodes that have lost their capacity as a result of the oxidation of sulfide sulfur. Most often, capacity loss is observed in batteries that are inactive for a long time (storage in a warehouse, long standing in a sludge, without preventive charge-discharge cycles). To restore the capacity of such batteries, they are poured with electrolyte, with the addition of 20-25 g / l of sodium sulfate and kept in this state for 3 to 10 hours. If this does not give results, then the batteries are repaired by opening the case. The recovered batteries are subjected to shaping and normal charging.
Batteries discarded due to mechanical damage or loss of capacity, repairs are performed by opening the case. Batteries are dismantled and defective elements (plates, separators, borons, housings, nuts, washers, etc.) are replaced. For this, a weld seam is cut off on a milling machine that connects the battery case to the top cover. The battery case is then clamped into a screw press and the plate assembly is removed. Unscrew the nuts securing the burs to the battery cover, remove the insulating washers and covers. After that, the block is disassembled into half-blocks, removed, washed and inspected between separators and each plate. The main internal defects of alkaline batteries, which reduce their capacity, are a break in the connecting contact strip, loss of active mass, closure of opposite plates by the dropped out active mass, rust deposits or as a result of warping of the plates when the separator is damaged. During repairs, corroded areas are protected and the condition of the active mass is checked.
Plates with dropped out active mass or damaged skeleton are rejected. The torn off contact strips are fixed by electric spot welding. Suitable plates are washed, dried and pressed into molds. Pressing is carried out to restore the size of the swollen plates and create a reliable electrical contact between the active mass and the plate body. Then the batteries are collected, painted, dried, covered with covers and charged-discharge cycles.
The repaired batteries are transported to the charging room, installed on racks, connected to batteries and filled with pre-prepared electrolyte. When electrolyte is poured into rinsed batteries, its density slightly increases. In 3-6 hours after pouring, it will decrease to normal, since the water remaining in the pores of the plates will dilute the electrolyte.
Depending on the type, alkaline batteries are produced with electrolyte filled or not filled. To prepare for the first charge, non-filled batteries are divided into groups depending on the value of the EMF. If E.D.S. non-filled batteries below 0.7 V, then to bring them into working condition, it is necessary to carry out 5-6 charge-discharge cycles. If E.D.S. batteries more than 0.7 V, then 2-3 cycles are enough for this. After dividing into groups, the batteries are filled with electrolyte with a temperature not higher than 30 ° C and left to soak the active mass of the electrodes for several hours. Before putting the batteries on the first charge, you must check the voltage on each of them. If the voltage turns out to be zero, then such batteries are discarded.
Normal charging current for nickel-iron and nickel-cadium batteries, a current is adopted, which is usually numerically equal to 0.25 of the nominal capacity .. The discharge in all cycles is produced by a current equal to 0.2 of the nominal capacity for a specified time or up to a voltage of 1 V.
During the first charge, the batteries are given a capacity equal to approximately 3 nominal capacities. This boosted charge improves battery life and increases the capacity of both plates. After the end of the charge, the batteries are switched on for discharge with a constant current. During the first discharge, the battery is usually not able to deliver capacity and the criterion for the final discharge is the lowest allowable voltage of 1 V. During the second training cycle, the batteries are again given increased capacity, and the discharge is carried out in the same way as in the first cycle. The third cycle is the control one. In this case, the battery is reported with a capacity of 1.5 times the nominal capacity.
The total operating time of the batteries can vary from 45 to 90 hours. After each charging and discharging mode, it is necessary to take breaks of 1-1.5 hours to cool the batteries. If the electrolyte temperature exceeds + 45 ° C, interrupt the charging and discharging mode and allow the battery to cool down. Batteries that, after a control cycle, give more than 80% of their rated capacity at discharge and whose voltage is at least 1 V, can be put into operation. Batteries with lower capacity and voltage are subjected to two more training cycles.
Batteries that have undergone repair with opening the case are charged in the same way as new ones. If the case was not opened during the repair, then the battery is subjected to one training charge-discharge control cycle. As a rule, several batteries are simultaneously charged on the site, to which, in addition to the usual number of batteries, three or four more batteries of the same type are added from among those repaired in advance. Batteries with a final voltage of 1.1 V are completed in one group, and with a voltage from 1.1 to 1 V - in another group. After that, the final discharge of the batteries is carried out with the normal charging current.
The sign of the end of the charge is a constant voltage of 1.8 +0.1 V for 30 minutes.
Batteries, which after depot repairs have a capacity of at least 70%, and after major overhaul at least 80% of the nominal, are installed in rubber covers and transferred to the installation position on the car.
5. Research part.
5.1. General Provisions.
In a number of locomotive depots, the restoration of alkaline batteries, the parameters of which do not meet the operational requirements, are being successfully carried out. The invention relates to the electrical industry and can be used in the repair of alkaline batteries.
There is a known method of repairing an alkaline battery by carrying out a discharge, washing with distilled water, introducing activating additives, removing crystalline deposits and harmful impurities, followed by activation by electrolysis in distilled water and carrying out control-training charge-discharge cycles in an alkaline electrolyte.
This method is complex, inefficient and does not provide a decrease in self-discharge, gas evolution and recovery of capacity and emf.
The closest in technical essence and the achieved results is a method for repairing an alkaline battery by treating separators and positive electrodes with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid, washing with water, neutralizing in an alkaline electrolyte and charging
This method ensures that the capacity is restored only by 30-50% of the nominal, i.e. not effective enough.
The purpose of the present invention (A.S. No. 1034559 of the chief expert of the sector of repair of diesel locomotives of the central heating station of the Ministry of Railways B.N. This is achieved by the fact that in the method of repairing an alkaline battery, by treating separators and positive electrodes with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid, washing with water, neutralizing in an alkaline electrolyte and charging, according to the invention, the density of the sulfuric acid solution is chosen equal to 1.25 - 1.27 g / cm 3, the separators are treated with this solution within 3 hours, and the positive electrodes within 20 - 30 seconds.
5.2 Recovery technology.
A battery with an increased capacity or increased self-discharge is discharged to zero, the electrolyte is drained, the top cover is closed, and blocks of positive and negative electrodes with separators are removed. The separators are treated with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.25 - 1.27 g / cm 3 for 3 hours. This time is necessary for the hydroxides of iron and magnetite to be converted into sulphate iron, partially dissolved in water and washed off from the surface of the separators, thereby restoring the dielectric properties of the separators and reducing the self-discharge value by several times. If the duration of the impregnation is less than 3 hours, a deposit of active mass, mainly iron compounds, remains on the surface of the separators. A further increase in the processing time over 3 hours has no effect on the quality of the separators; does not lead to an improvement in their dielectric properties.
Positive electrodes are treated with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.25 - 1.27 g / cm 3 for 20 - 30 seconds.
After treatment in a solution of sulfuric acid, the separators and positive electrodes are washed in water and neutralized in an alkaline electrolyte. Negative electrodes are treated with water immediately after disassembly, then treated in an aqueous alkali solution. After that, the electrodes are assembled with separators into blocks, installed in the housing, poured alkalized water, welded on the lid, poured alkalized water, pour electrolyte of normal density 1.17 - 1.19 g / cm 3, produce a charge, then a control discharge and a final charge.
Example. For testing, 46 batteries of the TPZHN-550 brand (one battery) were selected, which in their condition did not meet the technical requirements, incl. 27 batteries are zero (with increased self-discharge), 14 - with insufficient voltage (in the range from 0.2 to 0.8 V) and 5 polarized.
These batteries have been disassembled, repaired, assembled and tested.
The separators removed from the positive and negative electrodes were immersed in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.25 - 1.27 and held for 3 hours. Then they were washed in a stream of water in order to remove iron sulfate from their surface.
Positive electrodes (half blocks) were immersed in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.25 - 1.27 and held for 25 seconds, then immediately washed with water. In this case, iron sulfate was easily washed off from the surface of the electrodes (lamellas), and also partially from under the lamella grids, and then immersed together with separators into an alkaline electrolyte.
By appearance Before treatment, the positive electrodes had a black velvet surface (FeOH, FeOOH), and after treatment, a pure glossy silver-colored metal surface identical to the new one.
The mounted batteries were assembled, charged for 12 hours with a ten-hour current of 150A, had an EMF of 1.4 - 1.5 V, and when tested for self-discharge after 100 days, they had an EMF of 1.38 - 1.4 (usually they do not withstand even 10 days), had a capacity (at the first discharge) of 440 A and more - 27 batteries, and at 330 - 440 A - 6, 220 - 330 A - 9, 160 - 220 A - 4 batteries.
During the battery charging period, the temperature (at the end of the cycle) ranged from +29 to +38 0 С (at a room temperature of +12 0 С), which indicates the normal course of the charging process and the good condition of the batteries.
The repaired battery was tested for operability by running the diesel locomotive ten times (without recharging between starts). After the tenth start total stress at the battery terminals was 64V, and before the first start 65 V.
The repaired battery was found suitable for further operation on the locomotive as a source of electrical energy.
5.3 An example of calculating the annual economic effect.
The calculation was made according to " Methodical instructions by definition of economic efficiency new technology, inventions and rationalization proposals in railway transport ”.
The calculation formula is:
where E is the annual economic effect, rubles;
С 1, С 2 - operating costs per one battery per year, in basic and new versions, rubles;
Е Н - standard coefficient of efficiency of capital investments, Е Н \u003d 0.15;
K 1, K 2 - specific capital investments in production assets, respectively, in the basic and new versions, rubles;
A 2 - the number of batteries recovered in the depot per year, pcs.
After algebraic transformations, Formula 5.1 can be written in the following form:
From formula 5.2 it can be seen that when determining the economic effect, it is necessary and sufficient to calculate the changes only in those items and elements of operating costs and capital investments, which are directly affected by the application of the battery recovery method.
And today we will consider one recovery option using the example of alkaline batteries. I recently came across an alkaline battery produced soviet Union, voltage 9 volts, current 200 milliamperes, similar to the crown, only it can be charged.
This battery was produced 30 years ago and when I checked it with a multimeter, the voltage was zero, although I did not expect anything else. I opened the cap and there I found batteries of the d-0.55 type, such batteries were often used in autonomous civilian equipment during the Soviet era. To restore the charge of such a battery, I used the old old-fashioned method, which we will talk about today.

To start rechargeable batteries were removed from the case and cleaned with a damp cloth. It is easier when the alkaline battery has a cap for draining the alkali, then you can drain it, rinse the battery with hot water, then drain the water and fill the battery with 50% sulfuric acid solution, hold for 5 minutes (no more), then drain the acid, wash the battery several times hot water, pour lye and charge. But in my case, it's not that simple, since the batteries are sealed.

So, after cleaning, I did not separate the batteries from each other, I put them in a plastic bag and put them in the freezer. The batteries must be in the freezer for 2 days. Then they need to be taken out of the freezer and placed in an aluminum or tin container with water, then the water must be put on low heat (it is convenient to use a gas stove). We are waiting for the water to boil. We boil the batteries for 15 minutes (don't be afraid - they won't explode). Now we turn off the gas stove, but we do not take out the batteries, we wait 30 minutes until the water cools down and only then we take them out and rinse them with cold water. After rinsing, dry the water with a napkin (try to dry it completely), after which we warm up the batteries on the stove. For this procedure, we take a metal plate, put the batteries on the plate and heat it up at a temperature of 60-70 degrees. It takes about 5-10 minutes to warm up the batteries. Next, we wait until the batteries cool down, put them back where we got them from and charge them. Charging is not easy! 30 minutes AC batteries (see diagram).

AC current should be 1/5 of the total battery capacity. Then we turn off the variable voltage source and leave battery alone for 2 hours. After 2 hours, we take an ordinary stabilized source constant voltage and charge our battery as expected. That's all - the regeneration of the old battery is complete, by Artur Kasyan (AKA).
Discuss the article RESTORATION OF ALKALINE ACCUMULATORS