TCS stands for Traction control system and stands for traction control system or traction control system. This system has more than 100 years of history, during which it was first used in a simplified form not only on cars, but also on steam and electric locomotives.
The deep interest of automakers in the TCS system appeared only in the second half of the 60s of the twentieth century, due to the arrival in the auto industry electronic technology... Opinions on the use of the Traction Control System are not unambiguous, but despite this, the technology has taken root and has been actively used by all leading car manufacturers for about 20 years. So what is TCS in a car, why is it needed and why is it so widely used?
Electro-hydraulic traction control TCS is part of the active safety vehicle and is responsible for preventing the drive wheels from slipping on wet and other surfaces with reduced grip. Its task is to stabilize, level the course and improve grip on the road in automatic mode on all roads, regardless of speed.
Wheel breakdown in sliding occurs not only on wet and frozen asphalt, but also during sudden braking, starting from a standstill, dynamic acceleration, cornering, driving on sections of roads with different grip characteristics. In any of these cases, the traction control system will react accordingly and prevent the occurrence of an emergency.
The effectiveness of the Traction control system is evidenced by the fact that after its approbation on high-speed Ferrari cars it was adopted by Formula 1 teams and is now very widely used in motorsport.
How TCS works
TCS is not a fundamentally new and independent introduction, but only supplements and expands the capabilities of the well-known ABS - anti-lock braking systempreventing the wheels from locking during braking. The traction control system successfully uses the same elements that are at the disposal of ABS: sensors on the wheel hubs and the system control unit. Its main task is to prevent loss of traction of the drive wheels with the road, with the support of hydraulics and electronics that control the braking system and the engine.
The TCS workflow is as follows:
- The control unit constantly analyzes the rotation speed and the degree of acceleration of the driven and driven wheels and compares them. A sudden acceleration of one of the drive wheels is interpreted by the system processor as loss of traction. In response, he acts on the braking mechanism of this wheel and performs forced braking in automatic mode, which the driver only states.
- In addition, TCS also affects the engine. After receiving a signal to change the wheel speed from the sensors to the ABS control unit, it sends data to the ECU, which gives commands to other systems forcing the engine to reduce tractive effort. Engine power is reduced by delaying ignition, stopping sparking, or reducing fuel supply in a cylinder, and in addition, the throttle valve may be covered.
- The latest traction control systems can also affect the operation of the transmission differential.
The capabilities of TCS systems are determined by the complexity of their design, on the basis of which they make adjustments to the operation of only one of the vehicle's systems or several. With multilateral participation, the traction control system can use various mechanisms to influence the road situation, including the system that is most suitable for the given conditions.
Opinions and facts about TCS
Although many experienced drivers note that the traction control mechanism somewhat reduces the performance of the car, for an inexperienced car enthusiast, the Traction control system is an indispensable assistant, especially when control over the traffic situation, for example, during bad weather, is lost.
If desired, TCS is disabled with a special button, but before that, it is worth recalling once again the list of those advantages that become unavailable when disabled:
- easy start and good overall handling;
- high safety when cornering;
- prevention of drifts;
- reducing risks when driving on ice, snow and wet asphalt;
- deceleration of rubber wear.
The use of the traction control system also brings some economic benefits, since it reduces fuel consumption by 3-5% and increases the engine resource.
In this article, we will try to understand the principle of the car's braking systems - ABS, ESP and TSC.
How do ABS, ESP and TSC work?
The first systems that prevent the wheels from locking and allow the driver to steer too much on the brake pedal to drive a car were introduced more than thirty years ago. These anti-lock braking systems became known as ABS.ABS consists of wheel speed sensors, a brake pressure modulator and electronic unit management. The task of the sensors is to record the beginning of wheel blocking. As soon as this has happened, the signal is transmitted to the control unit, which gives the command to the modulator, which reduces the fluid pressure in the hydraulic system of the brakes. When the wheel is unlocked and starts to rotate again, the fluid pressure returns to its original value and again forces brakes to work.
The processes of braking and releasing the wheels will be cyclically repeated until the threat of blocking disappears. The driver feels aBS work by shocks transmitted to the brake pedal.
The wheels are also capable of slipping at the moment of the start of movement, during acceleration, in cases of vigorous movement on sections with surfaces of different adhesion properties. The desire to get rid of these shortcomings caused the appearance.
When the drive wheels begin to rotate faster than the driven ones, this is perceived by the processor as slipping. Further, two options are possible. First, the electronics will "strangle" the engine, not paying attention to how actively the driver presses the gas pedal; the second - the drive wheels are slowed down until they stop slipping and catch the tread on the coating. However, both scenarios usually "work".
 What is remarkable about the TCS is the ability of the system, which is an "add-on" to ABS, to independently control the engine and brakes of individual wheels. The designers were able to approach the development of another electronic assistant - the electronic stabilization program ESP (Electronic Stability Program)... In addition, the opportunity electronic control traction and brakes were used to simulate a differential lock.
What is remarkable about the TCS is the ability of the system, which is an "add-on" to ABS, to independently control the engine and brakes of individual wheels. The designers were able to approach the development of another electronic assistant - the electronic stabilization program ESP (Electronic Stability Program)... In addition, the opportunity electronic control traction and brakes were used to simulate a differential lock.
What are the disadvantages of ABS? This system by regulating the pressure brake fluid, protect the wheels from blocking and provide the driver with the opportunity to drive the car even during his panic actions. But getting out of critical situation he must himself, relying on his own skill and composure. And if that's not enough?
Example: the car enters a bend too far. high speed, and, depending on the direction of rotation, it is carried either into a ditch or onto oncoming lane... The driver brakes sharply in response and additionally turns the steering wheel in the direction of drift, wanting to remain on a safe trajectory. As a result - drift or skid, although ABS did not allow the wheels to slip.
If the car was equipped with ESP, this would not happen. ESP will reduce fuel delivery to match engine power and RPM, and with it, vehicle speed, to meet the needs of the situation. But the main thing is that ESP will select the braking forces for each wheel separately, and in such a way that the resulting braking force opposes the moment that tends to turn the car and keep it on the trajectory.
 If the rear axle starts to skid when entering a corner, ESP will brake the outer front wheel... This creates a stabilizing moment that returns the vehicle to a safe driving path. If the car's understeer is too low, which causes the front wheels to drift off the bend, ESP will slow down the inner rear wheel, helping the driver maintain control of the car.
If the rear axle starts to skid when entering a corner, ESP will brake the outer front wheel... This creates a stabilizing moment that returns the vehicle to a safe driving path. If the car's understeer is too low, which causes the front wheels to drift off the bend, ESP will slow down the inner rear wheel, helping the driver maintain control of the car.
For ESP to work, Yield, Lateral Acceleration and Steering Wheel Position sensors had to be added to the existing wheel sensors and software processor. As a result, ESP not only monitors the speed of rotation of each of the wheels and the pressure in the braking system, as does ABS, but also monitors steering movements, lateral acceleration of the car, its angular speed and controls the operating modes of the engine and transmission.
Traction control is a combination of mechanisms and electronic components of a car that are designed to prevent slipping of the driving wheels. TCS (Traction Control System) is the trade name for the traction control system that is installed on Honda vehicles. Similar systems are installed on cars of other brands, but they have different trade names: traction control TRC (Toyota), traction control ASR (Audi, Mercedes, Volkswagen), ETC system ( Range rover) other.
The activated TCS prevents the driving wheels of the car from slipping when starting to move, sharp acceleration, cornering, bad road conditions and fast lane changes. Consider the principle of operation of TCS, its components and general arrangement, as well as the pros and cons of its operation.
How TCS works
The principle of operation of the traction control systemGeneral principle The operation of the Traction Control System is quite simple: the sensors included in the system register the position of the wheels, their angular velocity and the degree of slippage. As soon as one of the wheels starts to slip, TCS instantly removes the loss of traction.
The traction control system deals with slippage in the following ways:
- Braking of skidding wheels. The braking system is activated at a low speed - up to 80 km / h.
- Reducing the torque of the car engine. Above 80 km / h, the engine management system is activated and changes the amount of torque.
- Combining the first two methods.
Note that Traction Control System is installed on cars with antilock braking system (ABS - Antilock Brake System). Both systems use the readings of the same sensors in their work, both systems pursue the goal of providing the wheels with maximum grip on the ground. The main difference is that ABS limits wheel braking, while TCS, on the contrary, slows down a rapidly rotating wheel.
Device and main components
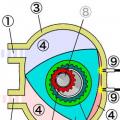
 ABS + TCS system diagram
ABS + TCS system diagram Traction Control System is based on anti-lock braking system elements. The anti-slip system uses electronic blocking differential, as well as the engine torque management system. The main components required to implement the functions of the TCS traction control system:
- Brake fluid pump. This component creates pressure in the vehicle's braking system.
- Switching solenoid valve and solenoid valve high pressure... Each drive wheel equipped with such valves. These components control braking within a predetermined loop. Both valves are part of the ABS hydraulic unit.
- ABS / TCS control unit. Manages the traction control system using built-in software.
- The engine control unit. Interacts with the ABS / TCS control unit. The traction control system connects it to work if the speed of the car is more than 80 km / h. The engine management system receives data from sensors and sends control signals to the actuators.
- Wheel speed sensors. Each wheel of the machine is equipped with this sensor. The sensors register the rotational speed, and then transmit signals to the ABS / TCS control unit.
 TCS on / off button
TCS on / off button Note that the driver can disable the traction control system. Usually on dashboard there is a "TCS" button that enables / disables the system. Deactivation of TCS is accompanied by illumination of the "TCS Off" indicator on the instrument panel. If there is no such button, the traction control system can be disabled by pulling out the appropriate fuse. However, this is not recommended.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of the Traction Control System:
- confident start of the car from a place on any road surface;
- stability of the car when cornering;
- traffic safety in various weather conditions (ice, wet canvas, snow);
- reduced tire wear.
Note that in some driving modes, the traction control system reduces engine performance, and also does not allow full control of the vehicle's behavior on the road.
Application
Traction control TCS is installed on vehicles japanese brand Honda. Similar systems are installed on the cars of other automakers, and the difference in trade names is explained by the fact that each automaker, independently of the others, developed an anti-slip system for its own needs.
The widespread use of this system has made it possible to significantly increase the level of vehicle safety while driving due to continuous control of grip with the road surface and improved handling when accelerating.
He will talk about what the ABS, ESP and TSC systems are like, what is the difference between them and what is their principle of operation.
It is simply impossible to imagine a modern foreign car without an auxiliary braking system or air conditioning, often it is no longer a luxury, but a necessary component of a complete set.
Accidental obstacle or accidental pressing of the brake pedal, skidding of the car can lead to loss of control and death. Every driver has had such a case.
What is ABS, TSC and ESP

The first systems that allowed the driver to align the car and keep the course of movement began to be established twenty years ago. ABS, or more in detail, are now not installed on cars, since newer ones came in their place, but still, they were the beginning of exchange rate stability systems.
There are three main components in ABS:
- Sensors for picking up the wheel speed;
- A device for changing the pressure in the brakes, for each wheel separately;
- Process control unit.
Not unimportant systemic is considered to be TSC, better known as ASC or ASR. Allows you to start from a place without slipping the driving wheels, it is very convenient to use when starting on snow or a track covered with ice. The system is based on the same sensors, only the control module has been modified, the wheel recognition function has been added to it. Thus, if during the start, the drive wheels rotate faster than the driven ones, then the control system perceives this as wheel slip. The control unit will reduce the engine speed, no matter how hard you press on the gas pedal, and the car will move smoothly.
A newer and more modernized ESP ("Vehicle Stability System") system can not only control the braking system, but also the engine. On SUVs, it was endowed with the ability to lock a differential. In cars bMW brands it's x-Drive, and on Mercedes it's 4-Matic. In addition to the standard sensors that were used in ABS, we also added side sensors, steering, skid and other sensors that make it clear to the system what is happening to the car while driving. Thus, when the system is turned off, all data is transmitted to the monitor on-board computer, and make it clear to the driver the situation on the road, the temperature outside the car and what the state of the road is. This greatly facilitates driving and gives confidence in the car, even without the system, you can make a decision in a given situation to maneuver.

Consider a situation when a car enters a turn and starts to skid to the side, turning the steering wheel in the direction of a skid, the driver will get out of the bend, and ABS will slow down as expected. But still, the last decision will remain with the driver, turn off the gas or slow down. In the presence of eSP systems, the situation will be completely different. First, it will reduce the fuel supply in order to reduce the rpm and engine power, because of this, the speed will decrease. Further, the system itself will determine which of the wheels should slow down more and which should not be touched at all, using the steering sensors, it will tell you in which direction it is worth turning the steering wheel to return to the previous driving trajectory.
Experienced drivers say that you should not play with these systems, that is, you should often press the brake pedal in a row, then the system will perceive it as emergency situation and will start working unnecessarily.
Video on how the ABS system works: