5 (100%) 5 votes
Ford focus 3 generations can rightfully be considered one of the leaders in the C class, recall that this generation has been sold since 2010 and in 2014 there was a slight restyling during which it changed slightly appearance and interior design. Running a little ahead, let's say that in 2018 the fourth generation of the Focus should appear on the market, the network is already full of information about the new product, as well as photos of pre-production versions. But back to our restyled version, today in Russia the car is sold in three body styles:
- five-door hatchback;
- sedan;
- station wagon.
Unfortunately, we went for the 3-door Ford Focus, as well as its sports versions ST and RS.
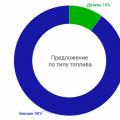
According to their technical specifications hatchback, sedan and station wagon are not much different, of course, if we are not talking about dimensions and volume luggage compartment... So the third generation Focus has front-wheel drive, three types of transmission, which we will talk about in more detail below and a rich line of engines, which includes:
- 1.6 liter gasoline engine 85 hp;
- 1.6 liter petrol engine with a capacity of 105 hp;
- 1.6 liter gasoline engine with a capacity of 125 hp;
- 1.5 liter turbocharged petrol engine with 150 hp
Of all the versions presented, in our opinion, the most interesting is the 1.6 liter engine with 125 hp. and 1.5 liter turbo delivering 150 hp.
It should be noted that earlier the car was also equipped with a 2.0 liter gasoline engine power of 150 hp, in new version its place was taken by a motor with a smaller volume, but equipped with a turbocharger. Recently, more and more manufacturers prefer turbocharged power unitssince they demonstrate better dynamics while using less fuel.
Available gearboxes
Now let's talk in more detail about which boxes are available on the 3rd generation Ford Focus and which one is better to choose based on reliability and ease of control.

As we have already said earlier, three types of gearboxes are installed on the car, each of which has its own pros and cons (we will also tell you about the advantages and disadvantages);
- 5-speed mechanics;
- 6-speed automatic;
- 6-stage.
The company's engineers decided to take a slightly different path than other manufacturers. While most companies are installing robotic transmissions on turbocharged versions, Ford engineers decided to equip atmospheric engines Robot Power Shift, while the turbocharged engine is equipped with a classic automatic.
If you are wondering which gearbox is better to buy a Focus with an automatic or robot or mechanics, we will now try to give you some idea.
To be honest, of the top three, we liked the work the most. classic machine, but the mechanics and the robot raised some questions.
Mechanics
There are no questions about the work of the mechanic, or rather the gear shifting, but the number of gears raised questions, but there are enough of them in the city, but when leaving the highway, there is a lack of 6th gear. Moreover, competitors have long been offering six gears.
Robot
Despite the fact that it has become much more reliable than the first versions, many motorists have concerns when buying a car with this type of gearbox. The Power Shift has its advantages and disadvantages, the disadvantages include jerky when switching from 1 to 2 and vice versa, which many can get when driving in a traffic jam. The second disadvantage is the cost of maintenance and the cost of repair in case of failure.
Price in 2018 and competitors
Today the cost of a car in Russia is:
- the price of a hatchback is 769,000 - 1,171,000 rubles;
- sedan price 916,000 - 1,181,000 rubles;
- the price of the station wagon is 926,000 - 1,191,000 rubles.
What competitors does Focus have
We can say from ourselves that we consider the main competitors korean manufacturers, which are completely similar, both in price and in technical characteristics
Gold 1 million box on the Getrag conveyor 2012
Transmission manufacturer Getrag has formed a joint venture with FoMoCo (Ford Motor Company) to produce preselective dual-clutch transmissions. As with DSG, they are of two types:
- with wet clutch WD (Wet Dual Clutch)
- with dry clutch DD (Dry Dual Clutch)
The checkpoint is identical in design dSG box with a wet clutch, the difference is only in the software and the number of gears: the DSG has a maximum of 7, while the PowerShift has 6. For VAG, the mechanical part and software were developed by Borg Warner, and for Ford - by Getrag and Luk. DSG works harder, with a slight jerk at the start and a well-felt engine braking under the throttle. With PowerShift, shifting is softer, almost like a classic hydromechanical automatic, but you can effectively brake the motor only in manual mode. The specialized club service DCT + carries out diagnostics and repairs of the Ford Focus 3 automatic transmission in Moscow with a guarantee.
Decoding of designations (Getrag)
DCL - longitudinal arrangement gearbox (L)
DCT - Transverse Gearbox (T)
6DCT / 7DCT - 6/7 speeds
250/450/750 - transmitted torque in N / m
For DCTs with low torque (up to 300 Nm), DD dry clutch boxes are installed. For more powerful cars there is a "wet" clutch WD (450/470, etc.).
3 types of transmissions are installed on Ford Focus 3: manual transmission, Ford automatic transmission Focus 3 robot (dry 6DCT250 and wet 6DCT450 for diesel versions).


6F35 assy


Valve body 6F35
6 stepped automatic transmission 6F30 / F35 / 6F50 / 6F15 from Ford - joint with General Motors. Mechanical part automatic transmission with a 6F35 torque converter is an almost complete analogue of the GM 6T40 / 6T45 gearboxes, spare parts for the production of which are unified as much as possible to reduce the development cost and differ in the electrical part, filters, pallets and outlets for installation on different layouts and other small nuances.
This gearbox model (6F35) is installed on almost all the lineup Ford (C-Max, Ecosport, Escape, Fiesta, Focus, Galaxy, Kuga, Mondeo, S-Max). If we take the Focus specifically, then the model with a 1.5 liter engine goes 6F35, with a 1.0 liter engine goes 6F15.
The transmission is manufactured at factories in the USA (Sterling Heights, Michigan, also Sharonville, Ohio) and in China. In general, the 6F family is a reliable and comfortable automatic transmission with 6 gears by modern standards. Differ from previous generations American 4-speed automatic transmissions in that preventive repair and cleaning of the system is required somewhat earlier, and, like most modern economical automatic transmissions, does not like aggressive driving.
Unlike the GM 6T series, the 6F series is tuned for a less dynamic and more gentle automatic transmission program. Ford regularly updates the automatic transmission ECU firmware, basically all updates are aimed at cutting down on drive and preserving the valve body and torque converter.
Since 2012, significant changes have been made to the design in the hydraulic and electrical parts, as well as in consumables... For example, the filter was made entirely of plastic, but retaining the double felt membrane. Better to change more often.
The filter is disposable and should be changed with every oil change. The oil change period strongly depends on the operating conditions. When driving quietly on the highway, the first oil change may be needed after about 80-100 thousand kilometers. But after prolonged loads near the limiting torque (at low speeds), in urban areas they may require an oil change after 20 thousand km. In general, as usual, on average, once every 60 thousand km. It is also worth preemptively repairing the torque converter, without waiting for it to fail (about 150 thousand km). The more aggressive the driving, the faster the clutch is consumed.
The entire 6F series is capricious to the oil level, does not have a dipstick and the oil level is checked using the overflow plug. And like all modern front-wheel drive gearboxes, it does not like loads with cold oil. Warming up the checkpoint in winter before driving is strictly recommended.
Typical Overhaul 6F35 / 6F15
The averaged typical repair automatic transmission Ford Focus 3 with automatic transmission 6F35 / 6F15 includes:
- obligatory repair of the torque converter
- valve body repair / cleaning with replacement of rings and seals
- set of clutches and steel discs
- replacement of damaged parts in the mechanical part
- consumables
DCT + specialized service carries out diagnostics, maintenance and repair of the automatic gearbox ff3 in Moscow in the club service. Full repair cycle without third-party contractors: torque converter (own workshop), valve body. There are repair and contract automatic transmissions 6F series, as well as spare parts for them. We have been working since 2009.
Prices for 6F35 / 6F15
Diagnostics: Free!
Contract (used) checkpoint:.
6DCT250 device (DPS6)

Powershift 6DCT250 is a product latest developments Gearbox with two clutches from Getrag. They combine the convenience of a conventional automatic transmission with the performance and high level of efficiency of manual transmissions. All Getrag transmissions with double clutch operate without interrupting the power flow and achieve a 4-8% reduction in CO2 emissions. Compared to classic torque converter automatic transmissions, the DPS6 with dry double clutch and electromechanical drive achieves a reduction in fuel consumption of up to 20% (compared to a conventional automatic transmission, not a car in general).
As usual, Getrag declares that 6DCT250 is filled with oil for life. But it is still worth changing to avoid problems ahead of time.
The 6-speed 6DCT250 transmission has been designed for front-wheel-transverse configuration in the segment compact cars and is designed for torque up to 280 Nm. It can be equipped separately with the system all-wheel driveas well as Start- / Stop function without hardware modification. Also DPS6 can be used in a hybrid drive (combined with an electric motor).
 Efficiency comparison manual transmission and 6DCT250
Efficiency comparison manual transmission and 6DCT250
Main features of 6DCT250:
- Uses a dry clutch that does not cool in oil. Efficiency increases.
- Oil filled and sealed for life (design life 10 years or 240,000 km), does not require periodic maintenance.
- Has a dry weight of 73 kg
- Faster gear changes and lower transmission losses.
- Electro-mechanical actuators eliminate the need for hydraulic lines.
- Dry clutch does not require cooling
- The complexity of the design can lead to problems and difficulties in repair
It is worth noting that manufacturers are switching from dry clutch transmissions to wet clutch transmissions due to higher reliability and thermal limitations (even in low torque applications, which is the area of \u200b\u200bdry clutches).
What Powershift 6DCT250 consists of:
As mentioned earlier, the DPS6 is mechanically composed of 2 mechanical boxes that interact using electrical equipment and electronics.
Dual clutches and dual input shafts

- There are 2 input shafts, one is hollow (blue) and the other is solid (yellow) and sits coaxially inside the hollow shaft.
- The inner shaft (yellow) has fixed gears for gears 1, 3, and 5; while the outer shaft (blue) has fixed gears for 2, 4, 6 and vice versa. Note that this shaft only has 2 gears, each of which is used for two gears.
- Each of these shafts is connected to a coupling via splines on the outside of the shaft.
- This arrangement allows for compact packing of both couplings.
- Unlike other couplings visible in manual boxes gears, at normal rest the clutch is held by springs (i.e. does not transmit torque) and must be actuated to close and held closed by a holding current applied to the actuator,
- The transmitting electronics ensures that only one clutch is closed at any time.
Output shafts

- The transmission has two output shafts (shown in blue). Contrary to initial considerations, they do not carry gears that match the input shafts. Instead, the gears they carry are determined by the order of the selector forks.
- The gears on the output shafts are not fixed, but are free. Like the manual transmission, they are equipped with synchronizers to match speeds and lock the gears.
- Gears 1, 3,4, 5, 6 and reverse are equipped with one synchromesh, and gear 2 is double syncronized.
- The second gear is connected to the rear gear on the same shaft (although both can rotate freely, they do it together).
- Note that the orange reverse gears on both output shafts are directly connected to each other. However, they do not interact with either the yellow or blue input shafts.
- As a result, the output shafts and input shafts are not in the same plane - instead, they are located in a triangular formation.
Differential

- Both output shafts transmit torque through the output gear to a common differential shaft (green).
- This differential is not in the same plane as the output shafts, it is biased again - 4 shafts are arranged in a parallelogram shape.
- A differential serves the same purpose as a mechanically equipped vehicle - it allows each of the driven wheels to rotate at a different speed (for example, when cornering).
Synchronizer sleeves and selector forks

- When discussing the output shafts, it was mentioned that none of the gears are attached to the shafts, but instead rotates freely.
- There are 4 synchronizers (and matching assemblies) that allow these freely rotating gears to match the speed of the output shaft and lock the gears. 3 of these bushings are used to engage the two gears (at different times) and 1 sleeve is used for only one gear.
- Each of these synchroniser arms has a corresponding shift fork that can move the sleeve either way (to lock the gear) or in the middle (to unlock the gear).
Up to this point, the components that have been reviewed are all familiar, as they closely resemble manual transmissions - rather, two gearbox, since we have two clutches, two input shafts and two output shafts. Only with a differential, both of these units are combined into one output. Next, we will consider the components that are just the whole chip of DCT Powershift 6DCT250.
Shear drives (actuators)

- For now we need to focus on the two electric motors present in the TCM as they provide rotary output from the TCM to drive the selector forks.
- The motors are of DC brushless design. They have built-in Hall sensors to determine the position of the rotor and count the number of rotations it has passed.
- Through a system of cylindrical gear wheels these rotating selector drums run at a specific angle (the range of travel for these drums is 200-290 degrees).
- The side switches have a slot cut into them. The selector fork has a tab that is located in this socket.
- The slot is angled to the ends of the stroke so that when the selector lever is rotated, the tab is forced perpendicular to the direction of rotation (i.e. parallel to the axis of the selector drum). If this is confused, to understand it, imagine how a screw converts the rotary motion of the screwdriver into direct motion.
- Thereby rotational movement generated by electric motors can be converted into moving selector forks back and forth ... This allows the selector forks to move the synchroniser sleeves forward or backward to lock and unlock certain gears.
- For comparison, in mechanical box The gear selector forks are manually operated using the gear shift levers.
Clutch actuators

- Like a shift actuator, a clutch actuator converts electric motor movement into lateral movement.
- And again, a brushless DC motor is used.
- As previously mentioned, the clutch is held open by spring pressure by default and does not transmit torque.
- To close the clutch, the motor rotates a worm gear, which pushes the clutch actuator.
- To keep the clutch closed, a holding current is applied to the motor.
- The following 2 animated images are a representative representation of how each of the clutches works. IN DSG principle same.
 |
 |
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
 TCM 6DCT250 control unit
TCM 6DCT250 control unit
The image for the shift actuators shows a pink part described as TCM. A little higher in the picture, which has input connectors from the ECU. The opposite side of this has the output of the 2 motors we saw earlier.
The TCM collects inputs from various sensors, evaluates the input, and controls the drives accordingly.
Inputs used by TCM include:
- Transmission distance (P / R / N / D / S / L, etc.)
- Vehicle speed
- Engine speed and engine torque
- Throttle position
- Engine temperature
- Temperature environment (to determine how viscous is transmission oil, for cold starts)
- Steering wheel angle (to avoid overload or underdrive when cornering)
- Brake inputs
- Input shaft speed (for both input shafts)
- Ratio (tilt) of vehicle from body control module (BCM)
The TCM controls the actuator motors with open loop control to provide adaptive control. This allows the TCM to identify and adapt to the following:
- Clutch engagement points (F1 fans will hear about "clutch bite point")
- Coefficient of adhesion friction
- Position of each synchronizer assembly
The information for the above is stored in non-volatile RAM in the TCM. This is what constitutes the transmission-specific control models studied.
Sensors
There are several sensors that collect and provide TCM information, both from the DCT and elsewhere in the vehicle. Those related to the DCT itself:
- Input Shaft Speed \u200b\u200bSensor (ISS Sensor) - Magneto-Resistive Sensor - one per input shaft
- Output shaft speed sensor (OSS sensor) - Magneto-resistive sensor again - one sensor attached to the differential
- Transmission range sensor (TR sensor) - for detecting the position of the selector lever and converting it into a PWM signal
Powershift DPS6 operating modes
Sport (S) and SelectShift (+/-)
- Sport (S) mode allows the engine to climb higher before upshifting.
- This allows the driver's requests to shift up and down with the +/- button be allowed.
- These are only "requests" because the TCM will evaluate this in relation to other inputs before shifting gears - for example, it prevents shifting more high revsto avoid hitting the cutoff
Parking mode (P)
 Parking mode
Parking mode
- A parking lot is fixed on the output shaft so that the output shaft does not rotate.
- The latch (pin) is spring loaded to ensure that it does not jump out if not disconnected.
- Both clutches are not actuated, so they both open automatically.
- Shift drives lock gears 1 and R - since pulling the car out of P will cause one of these gears to be selected.
- The user manual also recommends setting parking brake (hand brake) to ensure that this mechanism does not take off all the load on the vehicle (e.g. on a slope).
Hill Start Assist Mode
- This function is not an integral part of the 6DCT250, it also uses the braking system.
- When the vehicle is at a standstill on an incline greater than 3 degrees, assistance is activated.
- The braking system is pressurized to hold the vehicle until sufficient torque is established to move the vehicle. This may take 2-3 seconds.
- This allows the driver to move the right foot from the brake to the gas pedal without rolling away.
Neutral mode (N)
- The clutches will be disengaged when using the brakes.
- This improves fuel economy, improves landing gear downshifting and improves traction reliability.
Warning modes
- If the clutch temperature rises, warnings are generated to instruct the driver to stop on the vehicle until the clutch has cooled down. The driver can also accelerate the movement of the vehicle to cool the clutch through the airflow (the clutches can overheat when stopping and driving).
- To reduce clutch heating, the clutch will engage faster than normal and the engine torque will be reduced.
- If the clutch temperature exceeds 300 degrees Celsius, the clutches are disengaged.
- If one of the clutch drive motors fails, then the transmission adapts to this using only the gears on the other clutch.
- If the speed sensors do not work on the input shaft, then the gears on this shaft are locked.
- If the TCM itself or the TR sensor (transmission range) does not work, then both clutches are disengaged, and vehicle cannot be controlled.
- These failure modes will trigger the MIL / CEL (malfunction indicator / engine light).
6DCT250 Common Problems
Basically, problems are with the clutch, TCM, shift forks and, also encountered, problems with mechanical part Checkpoint (see examples of work). The input shaft oil seal is also leaking.
Consider the main ones related to the TCM block:
- Box jerks when switching from 1st to 2nd. Update needed software (firmware) of the TCM control unit.
- While working on dashboard The ESP lamp comes on and "Hill assist not available" appears.
- Transmissions disappear (not necessarily all), crawling mode is disabled
When installing a new Robot Control Module (TCM), it must be registered (VIN, Calibration). We provide this service too.
P0606 - Processor Malfunction
P07A3 - Stuck on the friction element A of the transmission.
P0702 - Electrical fault transmission control systems
P0707 - Low voltage input signal in the electrical circuit of the transmission range switch A
P0715 - electrical circuit of the sensor A of the input shaft speed
P0718 - intermittent signal in the electrical circuit of the input shaft speed sensor A
P0720 - Output Shaft Sensor Circuit
P0723 - intermittent signal in the electrical circuit of the output shaft sensor
P0805 - Clutch Position Sensor Electrical Circuit
P0806 - malfunction of the electrical circuit of the clutch position sensor
P0810 - clutch position sensor
P087A - Clutch Pedal Limit Switch Circuit
P087b - malfunction of the electrical circuit of the clutch pedal switch
P0882 - Low voltage input power signal
P0900 - open circuit of the clutch actuator
P0901 - quality problems of the clutch actuator
P090A - open circuit of the clutch actuator
P090b - violation of the parameters of the clutch actuator circuit
P0949 - Adaptive ASM Data Acquisition Failed.
P1719 - Invalid engine torque signal.
P1799 - Open circuit between TCM and ABS.
P2701 - Problems with the operation of the transmission friction element.
P2765 - malfunction of the input shaft rotation sensor (turbine)
P2802 - low voltage input signal in the electrical circuit of the transmission range
P2831 - malfunction of the shift fork A
P2832 - Problems with the quality of the shift fork
P2836 - Shift fork position B circuit
P285C - Parameters of the actuator circuit of the fork A
P2860 - Fork B Actuator Circuit Parameters
P2872 Jamming clutch A in engagement
P287A - Jammed clutch B
P287B - Gearshift Fork Calibration Not Registered
P090C - Clutch B Actuator Circuit Low Voltage
P0607 - characteristics of the control module
U0294 - Lost Communication With PMM
U0415 - Invalid data received from the ABS module
U1013 - Invalid monitoring data of the internal control module received from the TCM
U0101 - Lost Communication With TCM
U0028 Vehicle data bus
U0073 - the data bus of the control module is off
Clutch adaptation
Tips for the correct use of the 6DCT250 from Getrag
- Before putting the car on "P", the driver must hold down the brake pedal, raise the handbrake (parking brake), and only then can the rocker switch to "P".
- In modes "R", "D" and "S" it is prohibited to allow long work engine with the brake pedal depressed. In the position of the selector "D" and with the brake pedal depressed, the clutch of the Powershift DPS6 6DCT250 robot does not open completely and slips slightly, therefore, after a while, local overheating of the unit is possible. The company's specialists advise advised not to stand like this for more than two or three minutes and move the selector lever to "N" or "P".
- Towing a car in "N" mode is allowed up to 60 km / h.
Prices for 6F35 / 6F15 (automatic transmission with gas turbine engine)
Diagnostics: Free!
Partial oil change: 1500 (work) + flow
Complete oil change: 2000 (work) + consumption
Repair of the torque converter - 8-12 tr. Valve body repair - from 6 tr. Cap. repair: 10000 rub + s / h. Guarantee from 6 months.
Contract (used) checkpoint:.
Gold 1 million box on the Getrag conveyor 2012
Transmission manufacturer Getrag has formed a joint venture with FoMoCo (Ford Motor Company) to produce preselective dual-clutch transmissions. As with DSG, they are of two types:
- with wet clutch WD (Wet Dual Clutch)
- with dry clutch DD (Dry Dual Clutch)
The gearbox is identical in design to the DSG with a wet clutch, the only difference is in the software and the number of gears: the DSG has a maximum of 7, and the PowerShift has 6. For VAG, the mechanical part and software were developed by Borg Warner, and for Ford - Getrag and Luk ... DSG works harder, with a slight jerk at the start and a well-felt engine braking under the throttle. With PowerShift, the shifting is softer, almost like a classic hydromechanical automatic, but you can effectively brake the motor only in manual mode. The specialized club service DCT + carries out diagnostics and repairs of the Ford Focus 3 robot box in Moscow with a guarantee.
Decoding of designations (Getrag)
DCL - longitudinal arrangement of the checkpoint (L)
DCT - Transverse Gearbox (T)
6DCT / 7DCT - 6/7 speeds
250/450/750 - transmitted torque in N / m
For DCTs with low torque (up to 300 Nm), DD dry clutch boxes are installed. For more powerful cars there is a WD wet clutch (450/470, etc.).
Ford Focus 3 is equipped with 3 types of transmissions: manual transmission, automatic transmission with a torque converter, robot ff3 Powershift (dry 6DCT250 and wet 6DCT450 for diesel versions).
6DCT250 device (DPS6)

The Powershift 6DCT250 is the product of Getrag's latest dual-clutch transmission. They combine the convenience of a conventional automatic transmission with the performance and high level of efficiency of manual transmissions. All Getrag dual-clutch transmissions operate without interruption in power flow and achieve a 4-8% reduction in CO2 emissions. Compared to classic torque converter automatic transmissions, the DPS6 with dry double clutch and electromechanical drive achieves a reduction in fuel consumption of up to 20% (compared to a conventional automatic transmission, not a car in general).
As usual, Getrag declares that 6DCT250 is filled with oil for life. But it is still worth changing to avoid problems ahead of time.
The 6-speed 6DCT250 transmission has been developed for front-wheel drive-transverse configuration in the compact segment and is rated for torque up to 280 Nm. It can be equipped with a separate all-wheel drive system as well as a Start- / Stop function without equipment modification. Also DPS6 can be used in a hybrid drive (combined with an electric motor).
 Comparison of the efficiency of a manual transmission and 6DCT250
Comparison of the efficiency of a manual transmission and 6DCT250
Main features of 6DCT250:
- Uses a dry clutch that does not cool in oil. Efficiency increases.
- Oil filled and sealed for life (design life 10 years or 240,000 km), does not require periodic maintenance.
- Has a dry weight of 73 kg
- Faster gear changes and lower transmission losses.
- Electro-mechanical actuators eliminate the need for hydraulic lines.
- Dry clutch does not require cooling
- The complexity of the design can lead to problems and difficulties in repair
It is worth noting that manufacturers are switching from dry clutch transmissions to wet clutch transmissions due to higher reliability and thermal limitations (even in low torque applications, which is the area of \u200b\u200bdry clutches).
What Powershift 6DCT250 consists of:
As mentioned earlier, the DPS6 is mechanically composed of 2 mechanical boxes that interact using electrical equipment and electronics.
Dual clutches and dual input shafts

- There are 2 input shafts, one is hollow (blue) and the other is solid (yellow) and sits coaxially inside the hollow shaft.
- The inner shaft (yellow) has fixed gears for gears 1, 3, and 5; while the outer shaft (blue) has fixed gears for 2, 4, 6 and vice versa. Note that this shaft only has 2 gears, each of which is used for two gears.
- Each of these shafts is connected to a coupling via splines on the outside of the shaft.
- This arrangement allows for compact packing of both couplings.
- Unlike other clutches seen in manual transmissions, the clutch is held in normal rest by springs (i.e. it does not transmit torque) and must be actuated to close and held closed by a holding current applied to the actuator.
- The transmitting electronics ensures that only one clutch is closed at any time.
Output shafts

- The transmission has two output shafts (shown in blue). Contrary to initial considerations, they do not carry gears that match the input shafts. Instead, the gears they carry are determined by the order of the selector forks.
- The gears on the output shafts are not fixed, but are free. Like the manual transmission, they are equipped with synchronizers to match speeds and lock the gears.
- Gears 1, 3,4, 5, 6 and reverse are equipped with one synchromesh, and gear 2 is double syncronized.
- The second gear is connected to the rear gear on the same shaft (although both can rotate freely, they do it together).
- Note that the orange reverse gears on both output shafts are directly connected to each other. However, they do not interact with either the yellow or blue input shafts.
- As a result, the output shafts and input shafts are not in the same plane - instead, they are located in a triangular formation.
Differential

- Both output shafts transmit torque through the output gear to a common differential shaft (green).
- This differential is not in the same plane as the output shafts, it is biased again - 4 shafts are arranged in a parallelogram shape.
- A differential serves the same purpose as a mechanically equipped vehicle - it allows each of the driven wheels to rotate at a different speed (for example, when cornering).
Synchronizer sleeves and selector forks

- When discussing the output shafts, it was mentioned that none of the gears are attached to the shafts, but instead rotates freely.
- There are 4 synchronizers (and matching assemblies) that allow these freely rotating gears to match the speed of the output shaft and lock the gears. 3 of these bushings are used to engage the two gears (at different times) and 1 sleeve is used for only one gear.
- Each of these synchroniser arms has a corresponding shift fork that can move the sleeve either way (to lock the gear) or in the middle (to unlock the gear).
Up to this point, the components that have been reviewed are all familiar, as they closely resemble manual transmissions - rather, two gearbox, since we have two clutches, two input shafts and two output shafts. Only with a differential, both of these units are combined into one output. Next, we will consider the components that are just the whole chip of DCT Powershift 6DCT250.
Shear drives (actuators)

- For now we need to focus on the two electric motors present in the TCM as they provide rotary output from the TCM to drive the selector forks.
- The motors are of DC brushless design. They have built-in Hall sensors to determine the position of the rotor and count the number of rotations it has passed.
- These rotating selector drums pass through a spur gear system at a specific angle (the range of travel for these drums is 200-290 degrees).
- The side switches have a slot cut into them. The selector fork has a tab that is located in this socket.
- The slot is angled to the ends of the stroke so that when the selector lever is rotated, the tab is forced perpendicular to the direction of rotation (i.e. parallel to the axis of the selector drum). If this is confused, to understand it, imagine how a screw converts the rotary motion of the screwdriver into direct motion.
- Thereby rotational movement generated by electric motors can be converted into moving selector forks back and forth ... This allows the selector forks to move the synchroniser sleeves forward or backward to lock and unlock certain gears.
- In comparison, in a manual transmission, the selector forks are manually operated using the gear levers.
Clutch actuators

- Like a shift actuator, a clutch actuator converts electric motor movement into lateral movement.
- And again, a brushless DC motor is used.
- As previously mentioned, the clutch is held open by spring pressure by default and does not transmit torque.
- To close the clutch, the motor rotates a worm gear, which pushes the clutch actuator.
- To keep the clutch closed, a holding current is applied to the motor.
- The following 2 animated images are a representative representation of how each of the clutches works. In DSG, the principle is the same.
 |
 |
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
 TCM 6DCT250 control unit
TCM 6DCT250 control unit
The image for the shift actuators shows a pink part described as TCM. A little higher in the picture, which has input connectors from the ECU. The opposite side of this has the output of the 2 motors we saw earlier.
The TCM collects inputs from various sensors, evaluates the input, and controls the drives accordingly.
Inputs used by TCM include:
- Transmission distance (P / R / N / D / S / L, etc.)
- Vehicle speed
- Engine speed and engine torque
- Throttle position
- Engine temperature
- Ambient temperature (to determine how viscous a gear oil is for cold starts)
- Steering wheel angle (to avoid overload or underdrive when cornering)
- Brake inputs
- Input shaft speed (for both input shafts)
- Ratio (tilt) of vehicle from body control module (BCM)
The TCM controls the actuator motors with open loop control to provide adaptive control. This allows the TCM to identify and adapt to the following:
- Clutch engagement points (F1 fans will hear about "clutch bite point")
- Coefficient of adhesion friction
- Position of each synchronizer assembly
The information for the above is stored in non-volatile RAM in the TCM. This is what constitutes the transmission-specific control models studied.
Sensors
There are several sensors that collect and provide TCM information, both from the DCT and elsewhere in the vehicle. Those related to the DCT itself:
- Input Shaft Speed \u200b\u200bSensor (ISS Sensor) - Magneto-Resistive Sensor - one per input shaft
- Output shaft speed sensor (OSS sensor) - Magneto-resistive sensor again - one sensor attached to the differential
- Transmission range sensor (TR sensor) - for detecting the position of the selector lever and converting it into a PWM signal
Powershift DPS6 operating modes
Sport (S) and SelectShift (+/-)
- Sport (S) mode allows the engine to climb higher before upshifting.
- This allows the driver's requests to shift up and down with the +/- button be allowed.
- These are only "requests" because the TCM will evaluate this against the other inputs prior to gear shifting - for example, it prevents upshifts to avoid hitting the cutoff
Parking mode (P)
 Parking mode
Parking mode
- A parking lot is fixed on the output shaft so that the output shaft does not rotate.
- The latch (pin) is spring loaded to ensure that it does not jump out if not disconnected.
- Both clutches are not actuated, so they both open automatically.
- Shift drives lock gears 1 and R - since pulling the car out of P will cause one of these gears to be selected.
- The owner's manual also recommends installing a parking brake (handbrake) to ensure that this mechanism does not take off all the load on the vehicle (eg on a slope).
Hill Start Assist Mode
- This function is not an integral part of the 6DCT250, it also uses the braking system.
- When the vehicle is at a standstill on an incline greater than 3 degrees, assistance is activated.
- The braking system is pressurized to hold the vehicle until sufficient torque is established to move the vehicle. This may take 2-3 seconds.
- This allows the driver to move the right foot from the brake to the gas pedal without rolling away.
Neutral mode (N)
- The clutches will be disengaged when using the brakes.
- This improves fuel economy, improves landing gear downshifting and improves traction reliability.
Warning modes
- If the clutch temperature rises, warnings are generated to instruct the driver to stop on the vehicle until the clutch has cooled down. The driver can also accelerate the movement of the vehicle to cool the clutch through the airflow (the clutches can overheat when stopping and driving).
- To reduce clutch heating, the clutch will engage faster than normal and the engine torque will be reduced.
- If the clutch temperature exceeds 300 degrees Celsius, the clutches are disengaged.
- If one of the clutch drive motors fails, then the transmission adapts to this using only the gears on the other clutch.
- If the speed sensors do not work on the input shaft, then the gears on this shaft are locked.
- If the TCM itself or the TR (transmission range) sensor does not work, then both clutches are disengaged and the vehicle cannot be steered.
- These failure modes will trigger the MIL / CEL (malfunction indicator / engine light).
6DCT250 Common Problems
Basically, problems are with the clutch, TCM, shift forks and, also encountered, problems with the mechanical part of the gearbox (see examples of work). The input shaft oil seal is also leaking.
Consider the main ones related to the TCM block:
- Box jerks when switching from 1st to 2nd. TCM software (firmware) update required.
- During operation, the ESP lamp comes on on the dashboard and "Hill Assist Not Available" appears.
- Transmissions disappear (not necessarily all), crawling mode is disabled
When installing a new Robot Control Module (TCM), it must be registered (VIN, Calibration). We provide this service too.
P0606 - Processor Malfunction
P07A3 - Stuck on the friction element A of the transmission.
P0702 - Electrical malfunction of the transmission control system
P0707 - Low voltage input signal in the electrical circuit of the transmission range switch A
P0715 - electrical circuit of the sensor A of the input shaft speed
P0718 - intermittent signal in the electrical circuit of the input shaft speed sensor A
P0720 - Output Shaft Sensor Circuit
P0723 - intermittent signal in the electrical circuit of the output shaft sensor
P0805 - Clutch Position Sensor Electrical Circuit
P0806 - malfunction of the electrical circuit of the clutch position sensor
P0810 - clutch position sensor
P087A - Clutch Pedal Limit Switch Circuit
P087b - malfunction of the electrical circuit of the clutch pedal switch
P0882 - Low voltage input power signal
P0900 - open circuit of the clutch actuator
P0901 - quality problems of the clutch actuator
P090A - open circuit of the clutch actuator
P090b - violation of the parameters of the clutch actuator circuit
P0949 - Adaptive ASM Data Acquisition Failed.
P1719 - Invalid engine torque signal.
P1799 - Open circuit between TCM and ABS.
P2701 - Problems with the operation of the transmission friction element.
P2765 - malfunction of the input shaft rotation sensor (turbine)
P2802 - low voltage input signal in the electrical circuit of the transmission range
P2831 - malfunction of the shift fork A
P2832 - Problems with the quality of the shift fork
P2836 - Shift fork position B circuit
P285C - Parameters of the actuator circuit of the fork A
P2860 - Fork B Actuator Circuit Parameters
P2872 Jamming clutch A in engagement
P287A - Jammed clutch B
P287B - Gearshift Fork Calibration Not Registered
P090C - Clutch B Actuator Circuit Low Voltage
P0607 - characteristics of the control module
U0294 - Lost Communication With PMM
U0415 - Invalid data received from the ABS module
U1013 - Invalid monitoring data of the internal control module received from the TCM
U0101 - Lost Communication With TCM
U0028 Vehicle data bus
U0073 - the data bus of the control module is off
Clutch adaptation
Tips for the correct use of the 6DCT250 from Getrag
- Before putting the car on "P", the driver must hold down the brake pedal, raise the handbrake (parking brake), and only then can the rocker switch to "P".
- In modes "R", "D" and "S" do not allow the engine to run for a long time with the brake pedal depressed. In the position of the selector "D" and with the brake pedal depressed, the clutch of the Powershift DPS6 6DCT250 robot does not open completely and slips slightly, therefore, after a while, local overheating of the unit is possible. The company's experts advise advised not to stand like this for more than two or three minutes and move the selector lever to "N" or "P".
- Towing a car in "N" mode is allowed up to 60 km / h.
Examples of our work



The 3rd generation Ford Focus car replaced its predecessor, and did it quite successfully. The car has remained reliable, has become more modern, and is equipped with up-to-date electronics.
It is not the most expensive representative of the Ford carmaker, but it is the Focus that is among the best-selling cars in the world.
Automatic transmissions installed on the Focus 3 raise many questions. This is a rather controversial transmission option, which not everyone decides to buy. Although in practice the transmission works well, without any particular complaints about efficiency and durability.
Until now, motorists and experts cannot come to a consensus on changing the oil in an automatic transmission at Ford Focus 3. Therefore, you need to consider this issue in detail and give appropriate recommendations to car owners.
Replacement frequency
Let's start with the information provided by the official owner's manual for the 3rd generation Ford Focus. It indicates that the oil in the automatic transmission (PowerShift) lasts for the entire period. That is, you do not need to change it. Because of this, some difficulties arise regarding the replacement procedure for those who decide, contrary to the manual, to change the working fluid in the automatic transmission.
Experts advise still not to build on the official operating manual, but periodically change the lubricant in the gearbox. The only question is when you will be, and at what mileage the replacement will become a necessity.
In the case of an automatic transmission installed on a Ford Focus 3, replacement should be carried out every 100 thousand kilometers. This is the average optimum life of the lubricant.
If the operating conditions are difficult, then the service interval is reduced to 60 - 80 thousand kilometers. Practice shows that even in Russia Focuses 3 behave well, the boxes withstand the local climate and low quality roads. Therefore, most car owners will easily cover 100 thousand kilometers and even more.
Nothing eternal exists, so the statement about the "indestructibility" of the factory lubricant in the Focus automatic transmission cannot be considered fair. With use, the oil will lose its properties and characteristics. The box will begin to work intermittently, serious malfunctions and breakdowns will occur. As a result, expensive repairs will be required.
Given these facts, it is better to periodically change the lubricant and extend the life of the gearbox than to engage in complex and costly repairs. When heavy wear The automatic transmission may require its complete replacement.
Try to keep track of how many kilometers. you ran on old oil, periodically checking its condition. If you notice clear signs of fluid wear, be sure to send the car to a car service or change the lubricant yourself. In the case of a Ford Focus 3 car, oil change in a robotic automatic transmission can be done by hand with the appropriate tools, conditions and skills.
Volume and condition
Since the gearbox on the Ford Focus 3 model is a maintenance-free automatic transmission, there is no traditional dipstick. This somewhat complicates the procedure for measuring the volume of liquid in the crankcase, but does not make it impossible.
Consequences of working with worn-out oil
The automatic transmission installed on the Ford Focus 3 has a rather complex design and general organization of its work. It is difficult to repair it, and therefore it is in the interests of the car owner himself to maintain the operation of the box during the entire operational period.
There are several reasons for not adhering to the manufacturer's guidelines and still changing the lubricant in the transmission periodically. Gradual wear and further driving with oil that has lost its original properties leads to the following consequences:
- the internal components of the gearbox wear out faster;
- seizures are formed;
- corrosion appears;
- sealing elements wear out;
- working temperature changes;
- oil seals lose their properties;
- the likelihood of transmission breakdown increases.
So that you do not encounter such problems, and you do not have to pay a lot of money for the repair or replacement of automatic transmissions, monitor the condition of your car, change all consumables in time and do not forget about the importance of periodic preventive examinations.
Now there are almost no cars left where there would be no automatic transmission. Faults in her work occur in a couple more often than with mechanical transmission, however, this does not in any way affect the annually growing demand for cars with automatic transmission gear.
In this article, we take a look at the Ford Focus 3 and its modern included in the latest transmission called Power Shift. First, I will describe brief description the car itself, and then we will consider possible malfunctions automatic transmissions that can be encountered by drivers with this wonderful car.
Ford Focus 3New Power Shift transmission
What awaits us when buying this car model? Preselective Power Shift transmission with two clutch packs, EcoBoost turbo engines, electric amplifier, with the help of which the car independently parks, and also adheres to its lane line.
There is even a robotic electronic eye that can distinguish between the most common road signs... Any car enthusiast will be delighted with such unusual and useful innovations in the Ford Focus 3.
Some even recorded this model as a competitor for the A3. A car with an automatic transmission is currently breaking all sales records in Russia. Its popularity is the result of the successful work of highly qualified specialists.
The new Focus 3 family is a truly ambitious project from Ford Corporation. They are produced in Spain, Thailand, China, Germany, and of course, the USA and Russia. And on sale this model can be found in 129 countries around the world. During these 2 years, the car has shown itself perfectly and fully met the expectations of both developers and motorists around the world. Ford Focus 3, on which the automatic transmission is installed, is becoming an even more popular option among other representatives of this class.
Choosing between automatic and mechanics
The resources of modern gearboxes are quite high. Judge for yourself, up to 250 thousand kilometers at correct operation any box survives. To significantly extend the service life this mechanism it is imperative to study the rules for using the automatic transmission. This is a very important factor in car operation. So, the efficiency of the box largely depends on the driving style. Professional riders and just drivers who love fast driving, not in vain prefer "mechanics". Of course, modern machines can allow you to move quickly and dynamically. But if you look from the point of view of endurance, then city races in the mode "gas to the floor - a sharp brake" to the machine is absolutely contraindicated.
After all, it was not for nothing that only cars were equipped with an automatic transmission before executive class, whose task was the comfortable and safe delivery of passengers from one point to another. Well, now the automatic transmission can be found in every car: from a small car to an overall SUV. And it is not surprising that a person who takes a car with a powerful five-liter engine prefers to squeeze the maximum out of it, for which sooner or later you still have to pay by going over the box.
 Ford salon Focus 3
Ford salon Focus 3 Another problem that stands on the edge of the owners of cars on which the automatic transmission is installed is towing. The problem is as follows: the pump that supplies the lubricant naturally does not function when the engines are not running, while other parts are "forced" to rotate. Surely you know about the consequences of dry friction: parts wear out much faster and fray.
There are a few more very important subtletiesrelated to driving a car with an automatic transmission, for example, some inexperienced drivers think that when stopping in front of a traffic light, you need to turn on the "P" mode (parking mode), and when starting to coast down a hill, you must activate "neutral". Such a touching and strange concern is absolutely useless. Experienced car enthusiasts recommends to move the selector handle only twice during the entire trip: before starting the movement, set the position "D" (drive), and after the end of the trip - in the parking mode.
As an exception, there may be a situation when you need to tow a car out of a bog, deep snow or dirt. In such cases, forced automatic gearbox restrictions are usually used - this is position "1" or position "2". Of course, it is better to use third-party help with such a problem. Don't be suspicious - enjoy the convenience and comfort that automatic transmission gives us.
Possible faults in the automatic transmission
We propose to consider possible malfunctions of the automatic gearbox using the example of some of the most common breakdowns.
- If the automatic transmission does not go forward and the car is towing in place. This problem may be due to wear. friction discs, collar or broken clutch oil o-rings. If the automatic transmission does not want to go back, and only the 1st and 2nd speeds are turned on forward, then it is possible that the piston cuff is worn or broken.
- It also happens that the automatic transmission only goes forward and all the switches are present, but does not want to move backwards in any way, then most likely the piston rod of the brake band has broken. Or, again, wear of the friction layer or the piston cuff.
- When the automatic transmission does not go forward or backward, but when switching from the "P" or "N" mode to any other speed, there is not a tangible push to activate the gear. Or, the drive gear of the pump does not work, and therefore it has moved away and there is no clutch. With this problem, you need to check the presence of oil in the automatic transmission. Check the 1st speed valve, it may be stuck.
- If, when moving from a standstill, the car slips a little, but after a few seconds picks up normal speed, if you switch to other speeds. This indicates that the splines of the turbine wheel hub are worn out, as a result of which the gearbox shaft slips when high revs engine.
- Multimedia steering wheel new Ford Focus 3
Another common problem is clutch slippage when changing gears. This is due to the average clogging of the filter mesh. It may also be a low oil level or a faulty C1 clutch. If the car twitches while driving and slips from time to time, then the clutch is clearly out of order freewheel... Malfunctions in the automatic box can be very different. And you need to understand that such a complex mechanism as an automatic transmission does not need to be repaired on your own, you just need to take the car to a professional car service.