Felix Wankel is said to have invented the rotary engine as a 17-year-old. Recall that this engine provides excellent dynamic characteristics without a serious load on the engine and with low level vibrations. In general, in order to create such a complex structure, you need to study at the university and know almost everything about cars, and at that age, the guy hardly had a rich life experience behind him. But as practice and history show, everything in this world is possible.
Another "enemy" of this engine is that it runs on high revs with a low working curve, forcing it to always work close to its limits. It strengthens your vocation as a sports engine. Another "enemy" of this engine, perhaps the most ferocious, is a certain conservatism of the automotive environment. There is a certain susceptibility to new technology in all things accessory, but there is also a strong rejection of what is completely new, especially when new is related to engine design or operating mode.
However, the first drawings of the engine were presented by Wankel only in 1924, when he graduated from high school and began working in a technical publishing house. He later opened his own workshop and in 1927 introduced the first rotating piston engine. From that moment on, its engine begins its long journey through the engine compartment of many brands of cars.
The user of the most common, cheaper car will opt for a neighborhood mechanic who has learned his craft many times from experience, still young as an apprentice, and without more complex technical training. In these machine shops, the Wankel engine will still take a long time!
The rotary engine was invented by the German self-taught engineer Felix Wankel. Before we reveal how the Wankel engine works, let's go back in time to understand the origin of this engine. It was powered by a small 50 hp rotary engine.
NSU Spider
Unfortunately, during the Second World War, nobody needed a rotary engine, since it did not go through a sufficient "run-in" in the automotive community, and only after its completion, the miracle engine begins to "break out into the people." In post-war Germany, the first company to notice an interesting unit was NSU. It was the Wankel engine that was supposed to become the key feature of the model. In 1958, the development of the first project began, and in 1960 the finished car was shown at a conference of German designers.


This victory will not please other automakers, the rotary engine will subsequently be banned by the organizers. 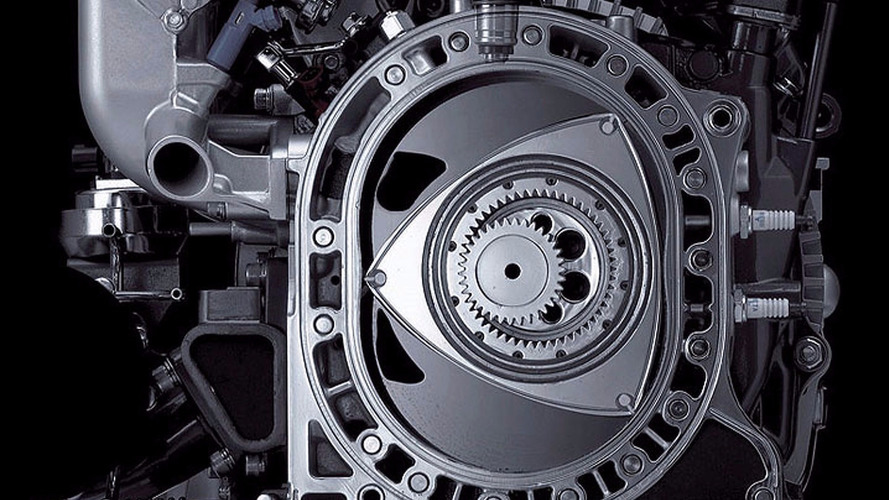
A rotating engine is very different from traditional engines, the piston movement of which is an alternative. A rotating motor consists of a triangular piston called a rotor. This piston or rotor has three edges that will distinguish between the three chambers. By performing a single rotation, the rotor achieves a four-stroke combustion cycle: intake, compression, expansion and exhaust.
NSU Spider at first caused only laughter and slight bewilderment among the designers. According to the declared characteristics, the Wankel engine developed only 54 hp. and many chuckled at this until they found out that the acceleration to 100 km / h for this 700-kilogram baby is 14.7 seconds, and the maximum speed is 150 kilometers per hour. Such characteristics have shocked many car designers. The engine definitely made a splash in the automotive environment, but Wankel didn't stop there.
The stator has an inlet. The air / fuel mixture is compressed by the rotor up to the spark plugs to ignite the fuel. The exhaust gases generated by this combustion are subsequently driven by the rotor to the exhaust duct. When the rotor rotates in the stator, it sets in motion gear trainas well as the motor shaft: the machine moves forward.
A rotating motor has only five moving parts, which is very good compared to a conventional motor. Moreover, compared to a conventional motor, the rotary motor is much more compact and lighter. With much less displacement, a rotary motor can deliver a high level of power. We allow ourselves to imagine the power delivered by a four-rotor motor.
NSU Ro-80
Interestingly, it was not the NSU Spider that made Felix Wankel popular, but his second car, the NSU Ro-80. It was introduced in 1967, immediately after the discontinuation of production previous model... The company decided not to hesitate and to develop the "rotary market" as quickly as possible. The sedan was equipped with a 1.0-liter engine, which developed a power of 115 horse power... The car, which weighed only 1.2 tons, accelerated to "hundreds" in 12.8 seconds and had maximum speed at 180 km / h. Immediately after its release, the car received the status of "Auto of the Year", the rotary engine began to be talked about as the engine of the future, and a huge number of automakers bought licenses for the production of Felix Wankel rotary engines.
No valves crankshaft or camshafts... In addition, there is almost no vibration, which allows the engine to be quieter. But now, if manufacturers have turned their backs on a spinning engine, there is a reason! Unfortunately, a rotary motor is less reliable than a reciprocating motor. Motor tightness is a big problem, the stator and rotor edges tend to expand over time. In addition, a rotary engine has more fuel and oil than a “normal” engine. For these last two reasons, customers do not lend themselves to this movement.
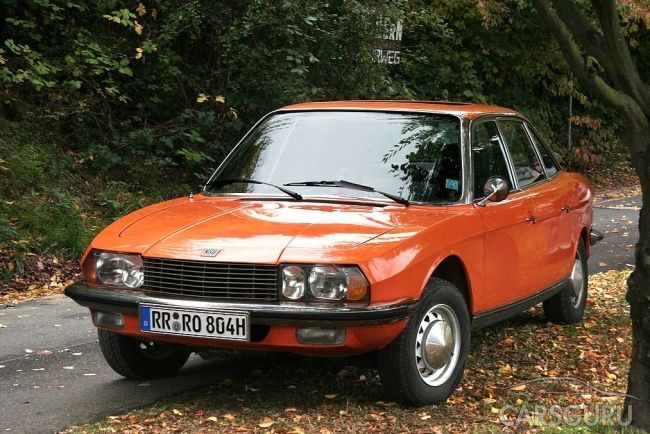

However, the NSU Ro-80 itself had a number of negative qualities, which were, without exaggeration, large-scale. Fuel consumption of the Ro-80 was between 15 and 17.5 liters per 100 km, and during the fuel crisis it was just awful. Moreover, inexperienced drivers very often "killed" these fragile engines so quickly that they did not even have time to drive two thousand kilometers. But, even in spite of this, the car was wildly popular, and the rotary engine strengthened its position.
Its rotating engine consistently consumed and consumed significant amounts of hydrocarbons, despite the Japanese firm's efforts to mitigate its gluttony. Let's say, however, that it's a little tainted by this annoying consumption and to a certain extent the reliability that needs to be asked.
Despite everything, the line is not impressive, although successful. On the inside, however, speech is different from the fact that little slivers of originality are not lacking. Thus, the reminders in the triangular shape of the motor rotors are numerous and good. Those located in the center of the head restraints, in particular, do not go unnoticed.
In 1970, at the Geneva Motor Show, Mercedes presented the C111 with a rotary engine. True, it was announced a year earlier, but it was only a prototype, which, however, had simply transcendental characteristics. The car was equipped with a 1.8-liter three-section engine with a capacity of 280 horsepower. The Mercedes C111 accelerated to 100 km / h in 5 seconds and had a top speed of 275 km / h.
And this is done with complete absence vibrations, which clearly show that the rotary is characterized by a very low number of moving parts by 3, 163 less than in a traditional six-cylinder. Should I add that this type of engine is lightweight and very compact? So don't rely on your younger couple to impress your parents, neighbors, or friends. In terms of acceleration, they also suffer from a lack of energy at low to medium speeds. In addition to its uncooled consumption, the rotary engine appears to be immune to mechanical accidents.
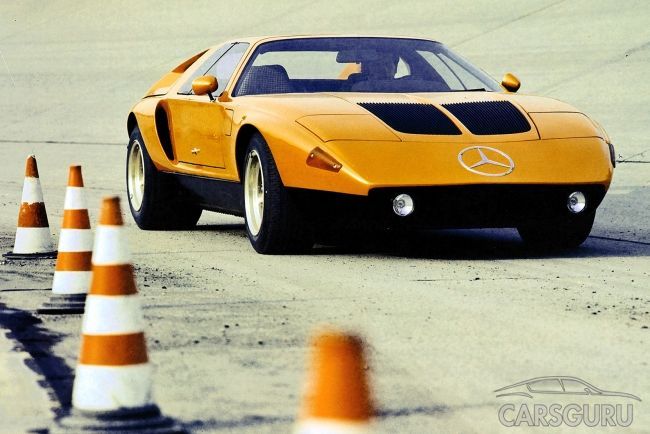

The version presented in Geneva even exceeded these figures: the maximum speed was 300 kilometers per hour, and it was possible to get to the 100 km / h mark in 4.8 seconds. At the same time, the rotary engine produced as much as 370 horsepower. This car was unique in nature and was simply enormous popularity among motorists, but Mercedes was not going to let the C111 on the conveyor again because of the over-gluttonous engine. Unfortunately, the car remained at the prototype stage, thereby almost burying the rotary engine.
On dashboard a warning light appeared indicating engine failure and it experienced a significant drop in power. This engine always hangs with it, which caused all the other builders to capitulate, i.e. its unreasonable consumption of gasoline and oil. Let's also offer a very original internal presentation and a more engaging practical aspect than many sports cars... Suspension comfort, on the other hand, is a concern, and it always seems that the damping is provided by springs in the wood with a characteristic shock.
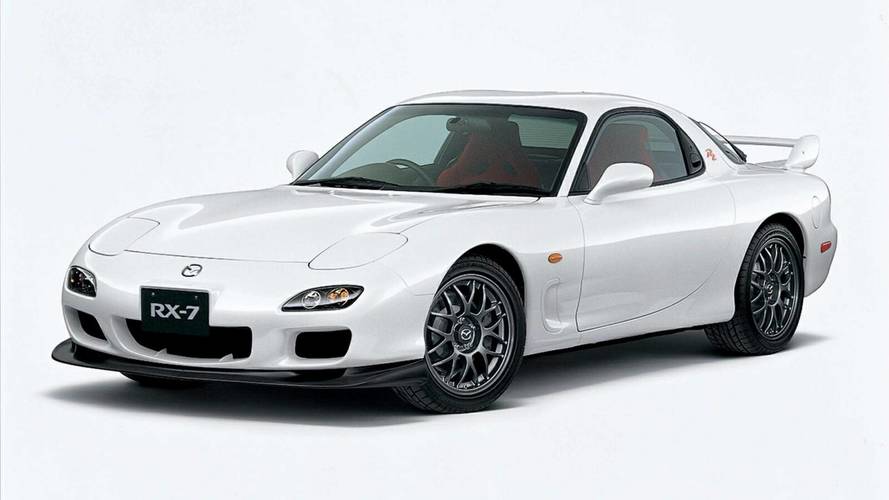
It would seem that the rotary engine has sunk into oblivion and finally disappeared from sight, if not for the Japanese, who closely watched the brainchild of Wankel. Mazda Cosmo Sport became the first car of the company from the Land of the Rising Sun to be equipped with this wonderful engine. In 1967, mass production of this car began, and it was not crowned with success - only 343 cars saw the light of day. This is due to mistakes in the design of the car: initially the Cosmo Sport had a 1.3-liter engine with a capacity of 110 horsepower, accelerated to 185 km / h using a 4-speed manual gearbox, but had a conventional braking system and, as it seemed to the developers, too short a wheelbase.
Green light Exceptional handling New engine A 4-door coupe Manual release Price prediction. Substantial consumption Low engine torque Charging rear seats Accessibility is limited at the rear. In a traditional four-stroke engine, four operations go through one cylinder: suction, compression, combustion and exhaust.
However, in a rotating motor, each of these four stages takes place in a different section of the stator. It looks like a top hat for each of the four races. In a piston engine, the expansion pressure created by burning the air / fuel mixture drives pistons that move back and forth inside the cylinders. Connecting rods and crankshaft converting this linear motion into the rotational motion required to pull the vehicle.
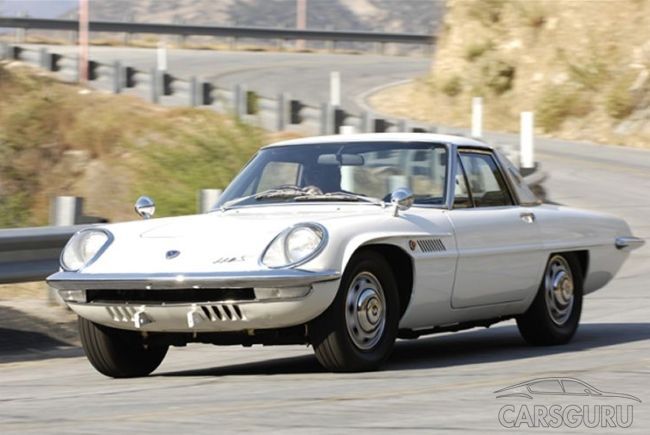

In 1968, the Japanese released the second Mazda Cosmo Sport series, which received a 128-horsepower rotary engine, a 5-speed manual gearbox, improved 15-inch brakes and a longer wheelbase. Now the car felt better on the road, accelerated to 190 km / h and had good sales. In total, about 1200 cars were produced.
In a rotating motor, there is no linear motion that needs to be converted. The pressure is contained in chambers created by various sections of the stator and the convex sides of the triangular rotor. When burned, the rotor immediately starts to rotate, thereby reducing vibration and increasing potential engine speed. increased efficiency, resulting in a much smaller engine with the same performance as a traditional piston engine.
The main component of a rotary engine is a triangular rotor that rotates inside an oval chamber, so that the three rotor blades constantly contact the inner wall of the chamber, forming three volumes of closed gases or combustion chambers. In fact, each of the three rotor blades acts like a piston. As the rotor moves inside the stator, the three chambers change shape and size, producing a pumping action.
Mazda Parkway Rotary 26
Mazda liked the engine of Felix Wankel so much that in 1974 the Parkway Rotary 26 was born - the world's only bus with a rotary engine. It was equipped with a 1.3-liter unit that produced 135 hp. from. and, importantly, had a low content harmful substances in the exhaust gases.

In the center of the rotor is a small gear wheel attached to the chamber. A larger wheel, toothed on the inside, mates with this stationary wheel, defining the path the rotor will follow inside the chamber. Since the rotor is mounted on the crankshaft, it rotates it with the same motion as the starting crank, so each rotation of the rotor corresponds to three turns of the crankshaft.
Each phase of the combustion process takes place in a different section of the chamber. James Watt, inventor steam engine with rotary motion, also conducted a number of studies on rotary motor internal combustion... Especially over the past 150 years, numerous inventors have proposed designs for rotating motors.
Together with 4-speed manual box gears, the 3-ton bus could easily pick up speed of 160 km / h and had enough roomy salon... The number 26 in the title meant the number seats on the bus, but there was also a luxury version for 13 people. The model featured a low vibration level and quietness in the cabin, which was ensured by the smooth operation of the rotary engine. The production of the model was completed in 1976, but, by the way, the car was quite popular.
Wankel did research by analyzing different types rotary motors and developed the optimal shape of the trochoidal stator. But the structure was complex as it also rotated the trochoidal stator and this made a rotating motor impractical.
Further improvements have resulted in emissions reductions in line with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and fuel costs by over 40%. The rotating engine was a reality meant to continue over time.
It's lighter. No pistons, connecting rods and crankshaft required, the main engine block of a spinning engine is smaller and therefore lighter, resulting in more maneuverability and better performance. It's less. For the same performance, a rotary engine is much smaller than a conventional engine. The small size of the rotary engine is not only an advantage in terms of weight, but also provides greater maneuverability, optimal drivetrain positioning and more space for the driver and passengers.
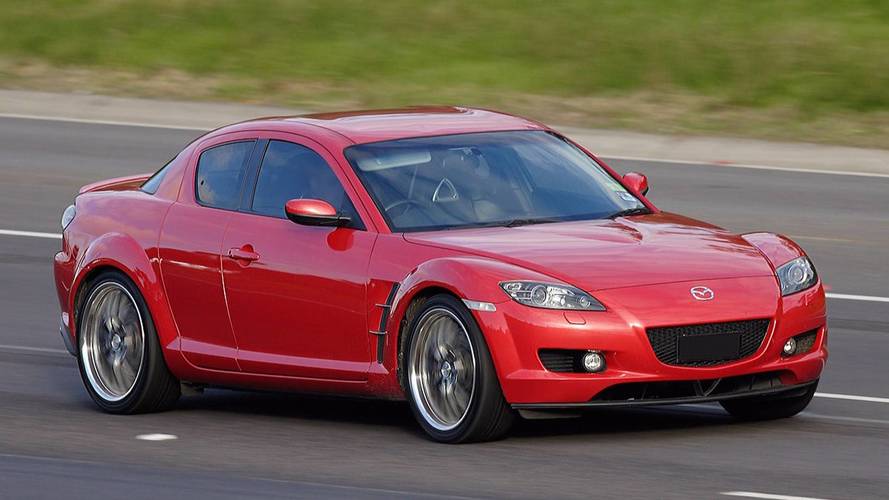
With the production of cars with a rotary engine "Mazda" did not stop until the XXI century. And the sporty four-seater rear-wheel drive coupe with swing doors without a pillar Mazda RX-8 has become a real icon for motorists. The latest version of the car was equipped with a 1.3-liter engine producing 215 hp. from. and a 6-speed automatic, as well as a 1.3-liter 231 hp engine. from. with a torque of 211 Nm and a 6-speed manual. In addition, it is undoubtedly the most beautiful member of the rotary family.
Rotary motors are also internally balanced to minimize vibration. More power The power output of a rotating engine is more uniform since each combustion event continues through 90 degrees of rotor rotation and that each rotation of the rotor corresponds to three crankshaft revolutions, each combustion event extends 270 degrees of crankshaft rotation. A single rotary engine then supplies power for three-quarters of the crankshaft rotation. In a single piston engine, instead, feed is only delivered to every quarter of each crankshaft rotation.
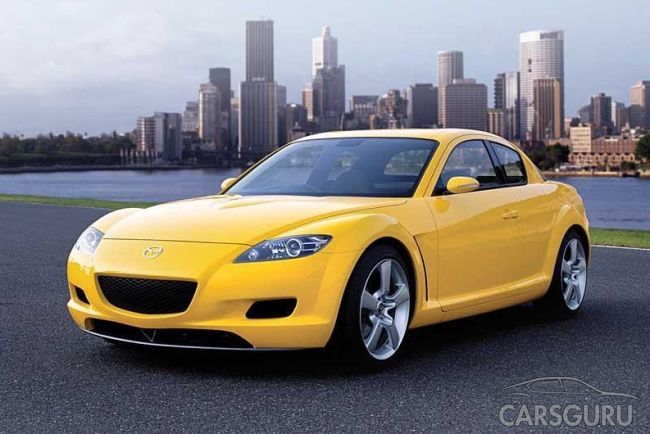

It seemed that the replacement RX-7 was the only production model with a rotary engine will remain a living symbol of this invention, but since 2004, coupe sales began to fall. So much so that by 2010 to reduce from 25,000 cars to 1,500 per year. Mazda tried to save the day, but the company's engineers were unable to fix all the problems - improve environmental friendliness, reduce weight, reduce fuel consumption and improve torque. In addition, the outbreak of the crisis forced the Japanese to abandon investing money in a project that does not bring returns. Therefore, in August 2011, it was announced that the Mazda RX-8 was discontinued.
Increased reliability A rotating engine has fewer moving parts than a four-stroke engine of similar performance. A two-rotor rotary engine has three main moving parts: two rotors and a crankshaft. The simplest four-cylinder engine also has at least 40 moving parts, including pistons, connecting rods, camshafts, valves, latches and rods for valves, a timing belt, gear wheels and crankshaft.
This is a new technical approach that has revolutionized the design of the rotary engine, combining it with excellent elegance, high performance and low fuel consumption and emissions. The double walled manifold maintains high exhaust temperatures, shortening the time it takes to heat up the catalyst. The new ultra-flat lubrication system lubricating oil The oil sump is only 40 mm deep, half the depth of conventional rotary engines.
"VAZ-2109-90"
Once there was a bike: they say, at a speed of 200 km / h "nine" of traffic police is catching up with a flying Mercedes. And many took this story as a joke. But there is some truth in every joke. And definitely in this funny story there is much more truth than lies. In Russia, cars with a rotary engine were also produced. In 1996, a prototype VAZ-2109-90 was developed with a high-power rotary piston engine. It was indicated that the car should surpass all car models in terms of dynamic and speed qualities. domestic production... Indeed, a 140-horsepower rotary engine was installed under the hood of the Nine, which accelerated the car to 100 km / h in just 8 seconds and had a maximum speed of 200 km / h. On top of that, they installed in the trunk fuel tank with a capacity of 39 liters, because the gas mileage was huge. Thanks to this, it was possible to travel from Moscow to Smolensk and back without refueling.

Later, 2 more "charged" modifications of the "nine" were presented: a rotary engine developing 150 horsepower and a forced version with 250 "mares". But because of such excess power, the units very quickly fell into disrepair - only 40 thousand kilometers. True, this type of car did not take root in Russia due to the high price of the car, high consumption fuel and high maintenance costs.
Rotary engine invented by Dr. Felix Wankel, or rather he was a co-author with Walter Freude. In 1957, they developed two models of similar rotary engines, but the Wankel engine found wider applications. This is why this engine is often also called Wankel engine or Wankel rotary engine.
A rotary engine, like the engine in your car, is an internal combustion engine, but its principle of operation is completely different from a conventional piston engine.
If in a piston engine, there are several (depending on the cylinders) working volumes (cylinder and piston), alternately performing their standard cycles - mixture intake, compression, ignition and exhaust, then in a rotary engine, the pistons are replaced by a rotor. (a working triangular organ in the form of an epitrochoid), which, depending on the angle of rotation, alternately, together with the body, participates in the same cycles listed earlier (intake, compression, ignition, ejection)
In this article, we will learn about how a rotary engine works, about its features and interesting facts associated with it, the advantages and disadvantages. Let's start our acquaintance with a rotary engine, with the principle of its operation.
The principle of operation of a rotary piston engine
Like a reciprocating engine, a rotary engine uses the pressure created by the combustion of a fuel / air mixture. As in a piston engine, the inlet is in communication with throttle, and graduation with exhaust system... If in a piston engine this pressure is generated in the cylinders, and then through the pistons, connecting rods is transmitted to the crankshaft, then in a rotary engine there are no transmission links. The triangular rotor in a rotary engine is a kind of piston rotating in a circle and transmitting torque to the output shaft.
In fact, the rotor, when rotating, divides the common chamber into three isolated ones, in the volume of each of these conventional chambers its own cycle occurs (intake, compression, ignition, release). As with a piston engine, rotary engines have only 4 strokes.
As a rule, even the simplest rotary engine uses two rotors. This design allows you to reduce knocking, increase the stability of the engine. If you look closely at the picture, you will see that one full turn rotor, corresponds to 3 turns of the shaft.
The heart of a rotary engine is the rotor. The rotor in this case is equivalent to pistons in conventional engine... The rotor is mounted on a shaft with a certain eccentricity. In fact, this displacement can be compared to a handle on a winch. Such an installation of the rotor allows the transmission of torque from it to the shaft.
As we have already said, the engine has 4 strokes, they change depending on the angle of rotation of the rotor. We will now take a quick look at each of these strokes in a rotary engine.
Intake of the fuel-air mixture in a rotary engine
The intake of the mixture begins at the moment when one of the tops of the rotor passes inlet valve in the case. At this time, the volume of the chamber expands, involving the fuel-air mixture into its expanding space. The moment the next rotor tip passes the intake port, the next stroke begins.
Compression of the fuel-air mixture in a rotary engine
As the rotor turns, the volume of the mixture entrained in the rotor decreases, which leads to an increase in pressure. Maximum pressure is formed when the fuel-air mixture is in the spark plugs area.
Combustion of fuel-air mixture
Candles are used to ignite the mixture, as in a piston engine. They ignite the mixture at the same time, that is, they work synchronously. Typically two spark plugs are used for a rotary engine. The use of two spark plugs is associated with the characteristics of the working volume. It seems to be stretched along the wall of the case, which is why it is more efficient to use two candles so that the mixture burns out more quickly and evenly. In the case of a single spark plug, the mixture will burn longer, if I may say so gradually, which will significantly lower the peak pressure during an explosion when the fuel / air mixture is ignited.
As a result, from the resulting pressure of the blast wave, a working force is obtained that turns the rotor on the eccentric of the shaft. The torque is transmitted to the output shaft. The rotor turns to the outlet opening exhaust gases.
Exhaust gas emission
As soon as the rotor of one of its vertices crosses the boundary of the outlet, the exhaust gas is emitted. The rotor by inertia, as well as by means of the second rotor, which operates asynchronously, continues to change its angle and moves with its top to the inlet. Here everything happens again from the pick-up beat to the ejection beat.
Rotary engine units (parts)
Next, we will talk about the constituent parts of a rotary engine, which will also partly help you in a more accurate understanding of the engine's operation. A rotary engine incorporates an ignition system, a power supply system, a cooling system, which are similar to those used in piston engines. Now for the unique details.
Rotary engine rotor

The rotor has three convex surfaces with grooved grooves. Deepening allows you to slightly increase the working volume. On the tops (corners) of the rotor there are sealing, unidirectional plates. It is they who are involved in the sealing between the rotor and the housing. There are also metal rings on each side of the rotor that separate the working chamber from the crankcase. In addition, the rotor has a ring gear in the center on one side. This crown is rigidly fixed to the rotor. It is through this gear train that the operating torque from the engine is transmitted.
Rotary engine housing
The rotary engine body is like a layered cake. It has its own covers, working chambers, dividing walls. The best way to understand the design of the case will be by looking at the picture.
It can be seen from it that the engine has two chambers, separated by a wall and covers on both sides. Everything else, of course, also matters, but what we have listed is paramount.
And now we will talk about the working chambers of the rotary engine housing.
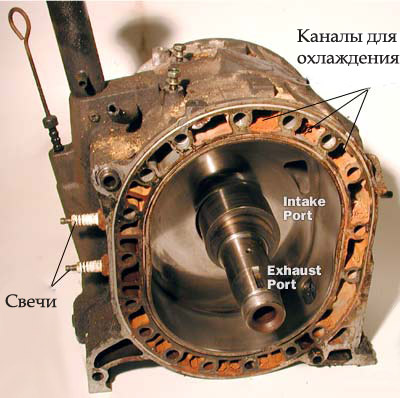
The internal cavity of the case is a complex shape resembling an oval. In fact, the oval has certain compensating ebbs, which ensure the sealing of all three chambers separated by the rotor, regardless of the angle of its rotation and the ongoing cycle. Each cycle has its own place in the rotary engine housing. Depending on the angle of rotation of the rotor, a corresponding cycle is performed, which is repeated at intervals every 360 degrees of rotation of the rotor
Outlets for the discharge of burnt gases are also located in the working chamber housing. Intermediate wall between cameras (pictured below)

holds the shaft in its central hole, seals with the rotors along the side walls, has elements of the cooling system, injection ports, guide bushings.
Rotary motor output shaft

The output shaft has eccentrics, in this case there are two of them, since two rotors are installed on the shaft, which work in antiphase, when one is in the exhaust gas cycle, the second is in the mixture intake cycle. The use of two rotors makes it possible to compensate for the beats during engine operation and, accordingly, reduce knocking. By displacing the eccentric and moving each of the rotors along the walls in the motor housing, they try to turn the shaft. As a result, a working torque is generated on it.
Advantages of a rotary engine
As we have already mentioned, the main advantage of a rotary engine is the absence of transmission links, namely connecting rods. In addition, the rotary engine does not require valves, valve springs, camshaft, timing belt, etc. All this ultimately affects the size and weight of the engine. That is why many aircraft manufacturers (for example Skycar, Schleicher) prefer rotary piston engines.
The advantages of a rotary engine, as we have already said, include a very good balance of parts in it. It can be compared to a boxer 4 piston engine.
A rotary engine for a longer time, in comparison with a piston engine, delivers torque to the output shaft. If for a rotary engine the power output to the shaft lasts about ¾ of a turn (270 degrees), then for a piston engine, torque is transmitted only for ½ a turn (180 degrees)
Since the rotor rotates only once in three shaft revolutions, this also affects the resource of the rotor, in contrast to piston engines, where the piston makes a full cycle per shaft revolution. Have japanese models cars, the engine resource can reach 300 t. km.
Disadvantages of rotary motors
So in modern world rotary engines are not widely used due to their low environmental friendliness.
Rotary engines consume more fuel due to the low operating pressures in the combustion chamber.
Rotary motors are not so common, which can be a problem in their repair and maintenance.
The engine has virtually no lubrication system. A certain amount of grease ( engine oil) is constantly thrown into the housing to the rotor. As a result, the engine has a significant oil consumption. Also, it must be of high quality mineral oil without additives, since "synthetics" burn out and form carbon deposits on the walls of the body.
Engines get much hotter than piston engines.
World renowned cars with rotary engines

(Pictured Mazda Cosmo Sport and Mazda RX8)
The Japanese company Mazda was a pioneer in the development of production vehicles with a rotary engine. So the first Mazda Cosmo Sport was released back in 1967. The next generation Mazda RX-7 went on sale in 1978. Perhaps it was one of the most successful machines with a rotary engine. AND last generation cars with a rotary engine are Mazda RX-8.
As a result, the most powerful non-turbocharged internal combustion engine was the Renesis engine from Mazda, with a volume of only 1.3 liters. It is he who has a record indicator of power to the working volume of the engine, namely 250 liters. from.
In recent years, Mazda has managed to significantly improve the performance of rotary engines. Engines are more environmentally friendly and do not require that much oil for lubrication.
Cars with a rotary engine were produced by other car manufacturers: Audi, Mercedes.
In the USSR, AvtoVAZ also produced a number of rotary engines. Rotary engines were installed on the car 21079 (1.3 liters 140 hp) and were planned for operation in the special services.
In the 90s, the following rotary engines VAZ-416, VAZ-426, VAZ-526 were created at the VAZ Scientific and Technical Center.
Rotary engine perspectives
The main prospects for rotary engines are associated with the transition to hydrogen fuel. Firstly, the problem of environmental friendliness is immediately solved, and secondly, rotary engines are practically not subject to detonation when operating with this type of fuel.